What is OS-Level Virtualization?
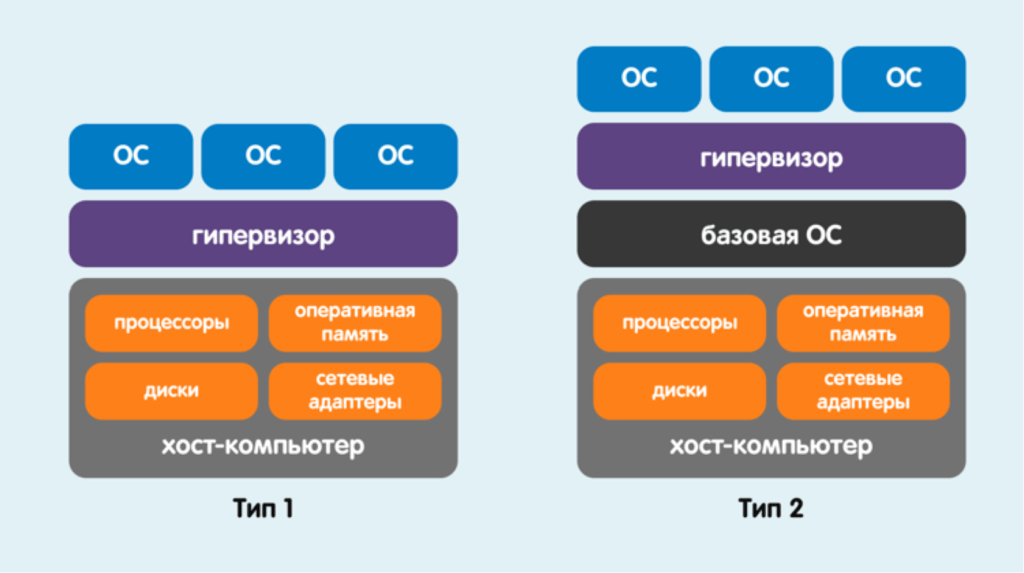
Operating System (OS)-level virtualization is a technology that allows you to create isolated virtual environments on a single physical server. This technology enables efficient use of server resources, increases security, and simplifies infrastructure management.
The main advantage of OS-level virtualization is the ability to run multiple isolated virtual environments on a single server. This significantly increases the density of server resource utilization, which leads to cost savings on the purchase of new hardware.
In addition, OS-level virtualization provides effective isolation of virtual environments from each other. This means that if one of the virtual environments malfunctions, it will not affect the operability of other environments.
To implement OS-level virtualization, special programs are used — virtual machines (VMs). Each virtual machine emulates the operation of a physical computer, allowing you to run operating systems, applications, and services on it.
Virtual machines run at the OS level and can be started and stopped independently of each other. This makes service management very flexible and convenient.
Thus, OS-level virtualization allows you to optimize the use of server resources, simplify infrastructure management, and improve data security. This technology is the foundation for building modern data centers and cloud services.