Setting up Database Replication on a MariaDB Server
Database replication is a powerful tool that allows you to create data backups and enhance system high availability. This article will guide you through setting up database replication on a server using MariaDB.
Before setting up replication, ensure that MariaDB is installed on your server. If not, install it using the following command:
sudo apt-get install mariadb-server
Now let’s proceed with the replication setup. Follow these steps:
1. Configuring the Primary Server:
- Open the MariaDB configuration file (usually located at
/etc/mysql/my.cnf) and add the following settings:
server-id=1
log_bin=/var/log/mysql/mariadb-bin
binlog_format=row
2. Create a replication user and grant it privileges:
CREATE USER 'repl'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'repl'@'%';
3. Perform a database dump and transfer it to the secondary server:
mysqldump -u root -ppassword mydatabase > mydatabase.sql
scp mydatabase.sql username@second_server_ip:/path/to/mydatabase.sql
4. Configuring the Secondary Server:
On the secondary server, open the configuration file and add the same settings as on the primary server. Then execute the following commands:
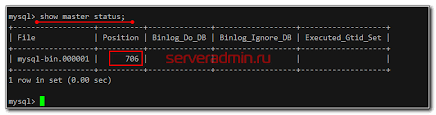
CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='primary_server_ip', MASTER_USER='repl', MASTER_PASSWORD='password', MASTER_LOG_FILE='mariadb-bin.000001', MASTER_LOG_POS=107;
START SLAVE;
After completing these steps, database replication should be successfully configured. Your server now has enhanced data protection and high availability.
Remember to regularly check the replication status and ensure that data backups are created on time. Good luck with the setup!

![How to Set Up Automated VDS Backups in [Platform/Location]](https://valebyte.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/leonardo_3b4910a9-300x169.jpg)
