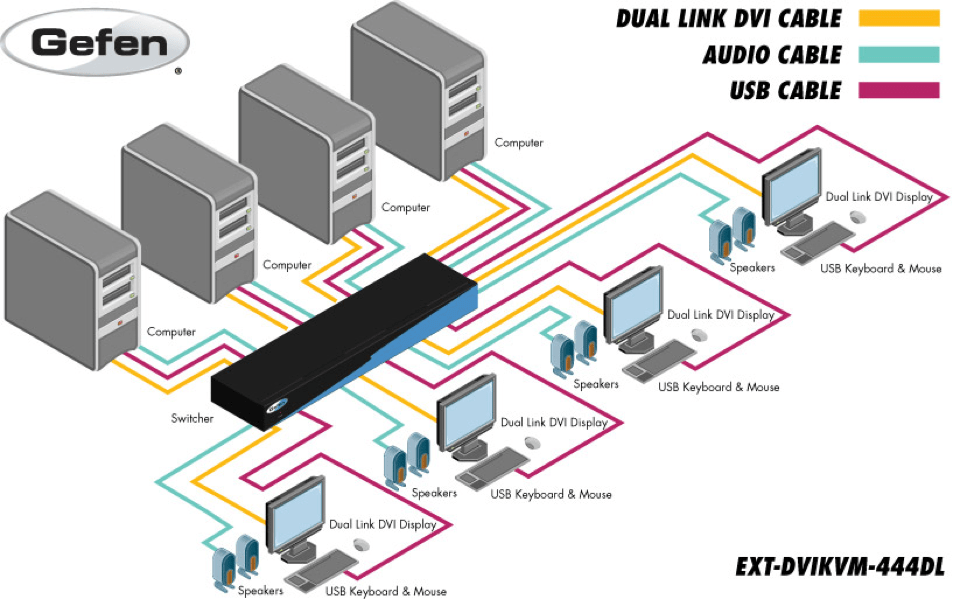
How does KVM work?
KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a hypervisor that allows you to virtualize operating systems at the Linux kernel level. This technology allows you to run multiple virtual machines on a single physical server, providing a high degree of isolation between them. But how exactly does KVM work? Let’s figure it out.
Hardware virtualization
The basic principle of KVM is based on hardware virtualization. This means that the server’s hardware, such as the processor, memory, and disk, is used to run virtual machines. The KVM hypervisor uses the processor’s hardware capabilities to create and manage virtual machines.
Virtualization mode
KVM uses a virtualization mode that allows virtual machines to be run with minimal overhead. This mode allows guest operating systems to execute instructions directly at the hardware level, providing high performance.
Resource management
KVM provides flexible resource management for virtual machines. An administrator can configure the number of processors, amount of memory, available disk space, and other parameters for each virtual machine separately.
Security
One of the key advantages of KVM is its high level of security. Each virtual machine is isolated from the others, which avoids potential vulnerabilities and attacks. The KVM hypervisor also provides data encryption and access control capabilities.
Conclusion
Thus, KVM is a powerful tool for virtualizing operating systems at the Linux kernel level. It provides high performance, flexible resource management, and a high level of security. If you need to run multiple virtual machines on a single physical server, KVM may be an excellent choice.