What’s the Difference Between a Full and Differential Backup?
For those involved in data backup, understanding the differences between a full and differential backup is an important aspect. Both methods allow you to save information in case of loss or damage, but the ways they are performed and subsequently restored differ.
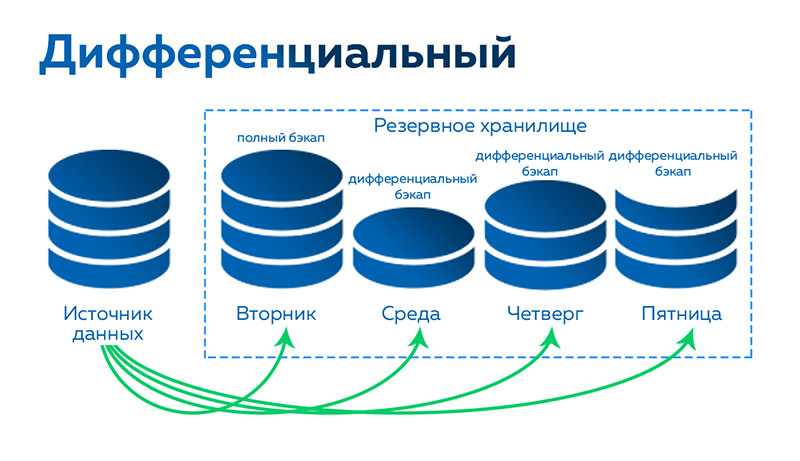
A full backup involves copying all data residing in the source selected for backup. This means that the entire volume of information will be copied to an external drive or remote server. This approach guarantees full data recovery in the event of loss of the original source.
On the other hand, a differential backup focuses on the changes that have occurred to the data since the last full backup. This reduces the time and volume required for copying data, as only the files and folders that have changed since the last backup are copied.
The main difference between a full and differential backup lies in the time and volume of stored data. A full backup requires more storage space on external devices, as the entire volume of information is copied each time. Differential backups save space and time, but data recovery may require access to all previous differential backups, which can slow down the recovery process.
The choice between a full and differential backup depends on the specific needs and requirements of the organization. If it is important to recover data as quickly and completely as possible, then it is better to choose a full backup. If significant changes occur infrequently, and saving space and time is critical, then it is better to opt for a differential backup.
In any case, it is important to regularly back up data to minimize the risk of data loss and ensure its reliable storage.