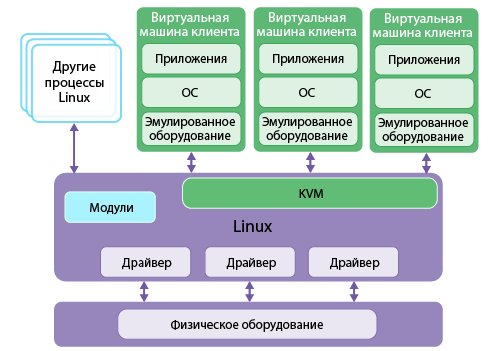
Virtual memory in KVM is a key component that ensures the efficient operation of a virtualized environment. KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is an open-source hypervisor that allows you to run multiple virtual machines on a single physical server.
How does virtual memory work in KVM? Let’s find out.
1. Basic Concepts
Before delving deeper into how virtual memory works in KVM, let’s break down the basic concepts:
Guest– this is a virtual machine that is running on KVM.Host– this is the physical server on which KVM and virtual machines run.Swap– an area of the hard drive used as virtual memory in KVM.
2. How Does Virtual Memory Work in KVM?
Virtual memory in KVM works as follows:
1. When a virtual machine (Guest) needs additional memory, and the physical memory on the server (Host) is exhausted, the KVM operating system begins to use an area of the hard drive (Swap) as virtual memory.
2. Data from physical memory is moved to Swap, freeing up space for the virtual machine to work.
3. When the virtual machine’s memory is freed, the data is returned from Swap to physical memory.
3. Benefits of Virtual Memory in KVM
Using virtual memory in KVM provides several benefits:
- Efficient use of server resources.
- Improved virtual machine performance.
- Flexibility in configuring virtual memory.
Now you know how virtual memory works in KVM and what benefits it provides. We hope that this information will be useful to you when working with a virtualized environment.