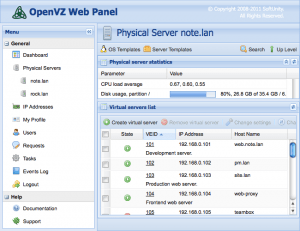
Example 1: Configure automatic backup of virtual machines using the built-in Proxmox VE tools or other backup solutions.
Example 2: Use Zabbix to monitor CPU load, memory usage, and disk space on all cluster nodes.
Example 3: Regularly check the Proxmox VE logs for errors or warnings. The logs are located in the /var/log/ directory.
tail -f /var/log/syslogExpert Tip: Create a Disaster Recovery Plan for your HA cluster. This plan should describe all the steps that need to be taken in the event of a serious failure that leads to data loss or cluster unavailability.
High availability is not just a technology, it is a process. Regular testing and maintenance are key factors for ensuring reliable operation of an HA cluster.
Author: John Doe, Senior Systems Administrator
3. Configure the Max Relocate and Max Restart parameters according to the requirements of your applications. Too many restart attempts can lead to cluster instability.
4. Monitor the HA cluster status using the web interface or command line. Make sure that all virtual machines are in the «started» state and that Failover is working correctly.
Example 1: If you have a virtual machine with a database that is critical for the operation of the website, assign it a high priority (for example, 50).
Example 2: If you have two virtual machines that work together (for example, a web server and an application server), combine them into one group (for example, webapp).
Example 3: If a virtual machine often fails, increase the Max Restart value so that Proxmox VE tries to restart it several times before giving up.
Expert Tip: Carefully plan your Failover strategy. Determine which virtual machines are the most critical and configure HA according to their requirements. Regularly test Failover to ensure that it is working.
Testing and Maintaining a High Availability Cluster
After setting up an HA cluster, you need to regularly test its performance and perform maintenance. This will ensure that Failover works correctly and that the cluster is ready for real failures. In this section, we will look at testing methods and recommendations for maintaining an HA cluster.
Failover Testing Methods
- Simulating a server failure: The easiest way to test Failover is to simulate a server failure. To do this, you can turn off one of the cluster nodes or cause a critical error that will cause it to reboot.
- Virtual machine migration: Check how quickly and smoothly the migration of a virtual machine from one node to another occurs.
- Checking the availability of services: Make sure that after Failover, all services running on the virtual machine remain available to users.
- Log analysis: Analyze the logs of Proxmox VE and other cluster components to make sure that Failover has passed without errors.
Example 1: To simulate a server failure, you can use the command shutdown -h now on one of the cluster nodes.
shutdown -h nowExample 2: To migrate a virtual machine, you can use the Proxmox VE web interface. Select a virtual machine and click the «Migrate» button.
Example 3: After Failover, check that the website running on the virtual machine is still available at its IP address or domain name.
Recommendations for Maintaining an HA Cluster
- Regularly update the software: Install the latest updates for Proxmox VE, operating systems on virtual machines, and other cluster components.
- Monitor the cluster status: Use monitoring tools such as Zabbix or Prometheus to track the status of cluster nodes, resource usage, and other important parameters.
- Perform backups: Regularly back up virtual machines and cluster configuration files.
- Check the performance of shared storage: Make sure that shared storage is accessible to all cluster nodes and that there is enough free space on it.
- Document all changes: Keep documentation of all changes made to the cluster configuration. This will help in troubleshooting and maintaining the cluster.
Example 1: Configure automatic backup of virtual machines using the built-in Proxmox VE tools or other backup solutions.
Example 2: Use Zabbix to monitor CPU load, memory usage, and disk space on all cluster nodes.
Example 3: Regularly check the Proxmox VE logs for errors or warnings. The logs are located in the /var/log/ directory.
tail -f /var/log/syslogExpert Tip: Create a Disaster Recovery Plan for your HA cluster. This plan should describe all the steps that need to be taken in the event of a serious failure that leads to data loss or cluster unavailability.
High availability is not just a technology, it is a process. Regular testing and maintenance are key factors for ensuring reliable operation of an HA cluster.
Author: John Doe, Senior Systems Administrator
2. Use groups to combine virtual machines that should be restarted together. For example, if a web application consists of multiple virtual machines (web server, database), combine them into one group.
3. Configure the Max Relocate and Max Restart parameters according to the requirements of your applications. Too many restart attempts can lead to cluster instability.
4. Monitor the HA cluster status using the web interface or command line. Make sure that all virtual machines are in the «started» state and that Failover is working correctly.
Example 1: If you have a virtual machine with a database that is critical for the operation of the website, assign it a high priority (for example, 50).
Example 2: If you have two virtual machines that work together (for example, a web server and an application server), combine them into one group (for example, webapp).
Example 3: If a virtual machine often fails, increase the Max Restart value so that Proxmox VE tries to restart it several times before giving up.
Expert Tip: Carefully plan your Failover strategy. Determine which virtual machines are the most critical and configure HA according to their requirements. Regularly test Failover to ensure that it is working.
Testing and Maintaining a High Availability Cluster
After setting up an HA cluster, you need to regularly test its performance and perform maintenance. This will ensure that Failover works correctly and that the cluster is ready for real failures. In this section, we will look at testing methods and recommendations for maintaining an HA cluster.
Failover Testing Methods
- Simulating a server failure: The easiest way to test Failover is to simulate a server failure. To do this, you can turn off one of the cluster nodes or cause a critical error that will cause it to reboot.
- Virtual machine migration: Check how quickly and smoothly the migration of a virtual machine from one node to another occurs.
- Checking the availability of services: Make sure that after Failover, all services running on the virtual machine remain available to users.
- Log analysis: Analyze the logs of Proxmox VE and other cluster components to make sure that Failover has passed without errors.
Example 1: To simulate a server failure, you can use the command shutdown -h now on one of the cluster nodes.
shutdown -h nowExample 2: To migrate a virtual machine, you can use the Proxmox VE web interface. Select a virtual machine and click the «Migrate» button.
Example 3: After Failover, check that the website running on the virtual machine is still available at its IP address or domain name.
Recommendations for Maintaining an HA Cluster
- Regularly update the software: Install the latest updates for Proxmox VE, operating systems on virtual machines, and other cluster components.
- Monitor the cluster status: Use monitoring tools such as Zabbix or Prometheus to track the status of cluster nodes, resource usage, and other important parameters.
- Perform backups: Regularly back up virtual machines and cluster configuration files.
- Check the performance of shared storage: Make sure that shared storage is accessible to all cluster nodes and that there is enough free space on it.
- Document all changes: Keep documentation of all changes made to the cluster configuration. This will help in troubleshooting and maintaining the cluster.
Example 1: Configure automatic backup of virtual machines using the built-in Proxmox VE tools or other backup solutions.
Example 2: Use Zabbix to monitor CPU load, memory usage, and disk space on all cluster nodes.
Example 3: Regularly check the Proxmox VE logs for errors or warnings. The logs are located in the /var/log/ directory.
tail -f /var/log/syslogExpert Tip: Create a Disaster Recovery Plan for your HA cluster. This plan should describe all the steps that need to be taken in the event of a serious failure that leads to data loss or cluster unavailability.
High availability is not just a technology, it is a process. Regular testing and maintenance are key factors for ensuring reliable operation of an HA cluster.
Author: John Doe, Senior Systems Administrator
1. Assign priorities to virtual machines depending on their importance. Critical virtual machines should have a higher priority.
2. Use groups to combine virtual machines that should be restarted together. For example, if a web application consists of multiple virtual machines (web server, database), combine them into one group.
3. Configure the Max Relocate and Max Restart parameters according to the requirements of your applications. Too many restart attempts can lead to cluster instability.
4. Monitor the HA cluster status using the web interface or command line. Make sure that all virtual machines are in the «started» state and that Failover is working correctly.
Example 1: If you have a virtual machine with a database that is critical for the operation of the website, assign it a high priority (for example, 50).
Example 2: If you have two virtual machines that work together (for example, a web server and an application server), combine them into one group (for example, webapp).
Example 3: If a virtual machine often fails, increase the Max Restart value so that Proxmox VE tries to restart it several times before giving up.
Expert Tip: Carefully plan your Failover strategy. Determine which virtual machines are the most critical and configure HA according to their requirements. Regularly test Failover to ensure that it is working.
Testing and Maintaining a High Availability Cluster
After setting up an HA cluster, you need to regularly test its performance and perform maintenance. This will ensure that Failover works correctly and that the cluster is ready for real failures. In this section, we will look at testing methods and recommendations for maintaining an HA cluster.
Failover Testing Methods
- Simulating a server failure: The easiest way to test Failover is to simulate a server failure. To do this, you can turn off one of the cluster nodes or cause a critical error that will cause it to reboot.
- Virtual machine migration: Check how quickly and smoothly the migration of a virtual machine from one node to another occurs.
- Checking the availability of services: Make sure that after Failover, all services running on the virtual machine remain available to users.
- Log analysis: Analyze the logs of Proxmox VE and other cluster components to make sure that Failover has passed without errors.
Example 1: To simulate a server failure, you can use the command shutdown -h now on one of the cluster nodes.
shutdown -h nowExample 2: To migrate a virtual machine, you can use the Proxmox VE web interface. Select a virtual machine and click the «Migrate» button.
Example 3: After Failover, check that the website running on the virtual machine is still available at its IP address or domain name.
Recommendations for Maintaining an HA Cluster
- Regularly update the software: Install the latest updates for Proxmox VE, operating systems on virtual machines, and other cluster components.
- Monitor the cluster status: Use monitoring tools such as Zabbix or Prometheus to track the status of cluster nodes, resource usage, and other important parameters.
- Perform backups: Regularly back up virtual machines and cluster configuration files.
- Check the performance of shared storage: Make sure that shared storage is accessible to all cluster nodes and that there is enough free space on it.
- Document all changes: Keep documentation of all changes made to the cluster configuration. This will help in troubleshooting and maintaining the cluster.
Example 1: Configure automatic backup of virtual machines using the built-in Proxmox VE tools or other backup solutions.
Example 2: Use Zabbix to monitor CPU load, memory usage, and disk space on all cluster nodes.
Example 3: Regularly check the Proxmox VE logs for errors or warnings. The logs are located in the /var/log/ directory.
tail -f /var/log/syslogExpert Tip: Create a Disaster Recovery Plan for your HA cluster. This plan should describe all the steps that need to be taken in the event of a serious failure that leads to data loss or cluster unavailability.
High availability is not just a technology, it is a process. Regular testing and maintenance are key factors for ensuring reliable operation of an HA cluster.
Author: John Doe, Senior Systems Administrator
1. Assign priorities to virtual machines depending on their importance. Critical virtual machines should have a higher priority.
2. Use groups to combine virtual machines that should be restarted together. For example, if a web application consists of multiple virtual machines (web server, database), combine them into one group.
3. Configure the Max Relocate and Max Restart parameters according to the requirements of your applications. Too many restart attempts can lead to cluster instability.
4. Monitor the HA cluster status using the web interface or command line. Make sure that all virtual machines are in the «started» state and that Failover is working correctly.
Example 1: If you have a virtual machine with a database that is critical for the operation of the website, assign it a high priority (for example, 50).
Example 2: If you have two virtual machines that work together (for example, a web server and an application server), combine them into one group (for example, webapp).
Example 3: If a virtual machine often fails, increase the Max Restart value so that Proxmox VE tries to restart it several times before giving up.
Expert Tip: Carefully plan your Failover strategy. Determine which virtual machines are the most critical and configure HA according to their requirements. Regularly test Failover to ensure that it is working.
Testing and Maintaining a High Availability Cluster
After setting up an HA cluster, you need to regularly test its performance and perform maintenance. This will ensure that Failover works correctly and that the cluster is ready for real failures. In this section, we will look at testing methods and recommendations for maintaining an HA cluster.
Failover Testing Methods
- Simulating a server failure: The easiest way to test Failover is to simulate a server failure. To do this, you can turn off one of the cluster nodes or cause a critical error that will cause it to reboot.
- Virtual machine migration: Check how quickly and smoothly the migration of a virtual machine from one node to another occurs.
- Checking the availability of services: Make sure that after Failover, all services running on the virtual machine remain available to users.
- Log analysis: Analyze the logs of Proxmox VE and other cluster components to make sure that Failover has passed without errors.
Example 1: To simulate a server failure, you can use the command shutdown -h now on one of the cluster nodes.
shutdown -h nowExample 2: To migrate a virtual machine, you can use the Proxmox VE web interface. Select a virtual machine and click the «Migrate» button.
Example 3: After Failover, check that the website running on the virtual machine is still available at its IP address or domain name.
Recommendations for Maintaining an HA Cluster
- Regularly update the software: Install the latest updates for Proxmox VE, operating systems on virtual machines, and other cluster components.
- Monitor the cluster status: Use monitoring tools such as Zabbix or Prometheus to track the status of cluster nodes, resource usage, and other important parameters.
- Perform backups: Regularly back up virtual machines and cluster configuration files.
- Check the performance of shared storage: Make sure that shared storage is accessible to all cluster nodes and that there is enough free space on it.
- Document all changes: Keep documentation of all changes made to the cluster configuration. This will help in troubleshooting and maintaining the cluster.
Example 1: Configure automatic backup of virtual machines using the built-in Proxmox VE tools or other backup solutions.
Example 2: Use Zabbix to monitor CPU load, memory usage, and disk space on all cluster nodes.
Example 3: Regularly check the Proxmox VE logs for errors or warnings. The logs are located in the /var/log/ directory.
tail -f /var/log/syslogExpert Tip: Create a Disaster Recovery Plan for your HA cluster. This plan should describe all the steps that need to be taken in the event of a serious failure that leads to data loss or cluster unavailability.
High availability is not just a technology, it is a process. Regular testing and maintenance are key factors for ensuring reliable operation of an HA cluster.
Author: John Doe, Senior Systems Administrator
Ceph is the most complex, but also the most productive and reliable solution for shared storage. Configuring Ceph is beyond the scope of this article and requires a separate guide. Proxmox VE has built-in integration with Ceph, which simplifies the setup process.
Example 1: When using NFS, make sure that the latest version is installed on the NFS server. Older versions of NFS may have performance and security issues.
Example 2: When using iSCSI, use CHAP (Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol) to authenticate between the iSCSI Initiator and Target. This will increase storage security.
Example 3: When using Ceph, use at least three monitors (MON) and three managers (MGR) to ensure high availability of the Ceph cluster.
Expert Tip: Before choosing a type of shared storage, evaluate the performance, reliability, and scalability requirements of your cluster. Test different options to choose the most suitable solution.
| Storage Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| NFS | Easy to configure | Low performance | For small clusters with low requirements |
| iSCSI | Higher performance than NFS | More complex configuration than NFS | For medium-sized clusters |
| Ceph | High performance, reliability and scalability | Complex configuration | For large clusters with high requirements |
Failover Configuration for Virtual Machines
After configuring shared storage, you need to configure Failover for virtual machines. Proxmox VE provides convenient tools for managing HA resources. In this section, we will look at how to enable and configure HA for virtual machines.
Enabling HA for a Virtual Machine
1. Select the virtual machine for which you want to enable HA in the Proxmox VE web interface.
2. Go to the «HA» tab.
3. Click the «Enable HA» button.
4. Configure HA parameters:
- Priority: The priority of the virtual machine during Failover. Virtual machines with higher priority will be restarted first.
- Group: Virtual machine group. Virtual machines in the same group will be restarted together.
- Max Relocate: The maximum number of attempts to restart the virtual machine on another node.
- Max Restart: The maximum number of restarts of the virtual machine on the same node.
5. Save your changes.
Managing HA Resources Using the Command Line
Proxmox VE also provides command-line tools for managing HA resources. This can be useful for automating HA configuration or troubleshooting.
1. Adding an HA resource:
ha-manager add vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager add vm:1002. Removing an HA resource:
ha-manager remove vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager remove vm:1003. Changing HA resource parameters:
ha-manager set vm:<VMID> --priority <priority> --group <group>For example:
ha-manager set vm:100 --priority 2 --group mygroup4. Viewing the HA cluster status:
ha-manager statusRecommendations for Configuring HA
1. Assign priorities to virtual machines depending on their importance. Critical virtual machines should have a higher priority.
2. Use groups to combine virtual machines that should be restarted together. For example, if a web application consists of multiple virtual machines (web server, database), combine them into one group.
3. Configure the Max Relocate and Max Restart parameters according to the requirements of your applications. Too many restart attempts can lead to cluster instability.
4. Monitor the HA cluster status using the web interface or command line. Make sure that all virtual machines are in the «started» state and that Failover is working correctly.
Example 1: If you have a virtual machine with a database that is critical for the operation of the website, assign it a high priority (for example, 50).
Example 2: If you have two virtual machines that work together (for example, a web server and an application server), combine them into one group (for example, webapp).
Example 3: If a virtual machine often fails, increase the Max Restart value so that Proxmox VE tries to restart it several times before giving up.
Expert Tip: Carefully plan your Failover strategy. Determine which virtual machines are the most critical and configure HA according to their requirements. Regularly test Failover to ensure that it is working.
Testing and Maintaining a High Availability Cluster
After setting up an HA cluster, you need to regularly test its performance and perform maintenance. This will ensure that Failover works correctly and that the cluster is ready for real failures. In this section, we will look at testing methods and recommendations for maintaining an HA cluster.
Failover Testing Methods
- Simulating a server failure: The easiest way to test Failover is to simulate a server failure. To do this, you can turn off one of the cluster nodes or cause a critical error that will cause it to reboot.
- Virtual machine migration: Check how quickly and smoothly the migration of a virtual machine from one node to another occurs.
- Checking the availability of services: Make sure that after Failover, all services running on the virtual machine remain available to users.
- Log analysis: Analyze the logs of Proxmox VE and other cluster components to make sure that Failover has passed without errors.
Example 1: To simulate a server failure, you can use the command shutdown -h now on one of the cluster nodes.
shutdown -h nowExample 2: To migrate a virtual machine, you can use the Proxmox VE web interface. Select a virtual machine and click the «Migrate» button.
Example 3: After Failover, check that the website running on the virtual machine is still available at its IP address or domain name.
Recommendations for Maintaining an HA Cluster
- Regularly update the software: Install the latest updates for Proxmox VE, operating systems on virtual machines, and other cluster components.
- Monitor the cluster status: Use monitoring tools such as Zabbix or Prometheus to track the status of cluster nodes, resource usage, and other important parameters.
- Perform backups: Regularly back up virtual machines and cluster configuration files.
- Check the performance of shared storage: Make sure that shared storage is accessible to all cluster nodes and that there is enough free space on it.
- Document all changes: Keep documentation of all changes made to the cluster configuration. This will help in troubleshooting and maintaining the cluster.
Example 1: Configure automatic backup of virtual machines using the built-in Proxmox VE tools or other backup solutions.
Example 2: Use Zabbix to monitor CPU load, memory usage, and disk space on all cluster nodes.
Example 3: Regularly check the Proxmox VE logs for errors or warnings. The logs are located in the /var/log/ directory.
tail -f /var/log/syslogExpert Tip: Create a Disaster Recovery Plan for your HA cluster. This plan should describe all the steps that need to be taken in the event of a serious failure that leads to data loss or cluster unavailability.
High availability is not just a technology, it is a process. Regular testing and maintenance are key factors for ensuring reliable operation of an HA cluster.
Author: John Doe, Senior Systems Administrator
5. Connect the LUN to each Proxmox VE node.
6. Add an iSCSI storage in Proxmox VE. In the Proxmox VE web interface, select «Datacenter» -> «Storage» -> «Add» -> «iSCSI». Specify the Target, LUN, and other required parameters.
Configuring Ceph
Ceph is the most complex, but also the most productive and reliable solution for shared storage. Configuring Ceph is beyond the scope of this article and requires a separate guide. Proxmox VE has built-in integration with Ceph, which simplifies the setup process.
Example 1: When using NFS, make sure that the latest version is installed on the NFS server. Older versions of NFS may have performance and security issues.
Example 2: When using iSCSI, use CHAP (Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol) to authenticate between the iSCSI Initiator and Target. This will increase storage security.
Example 3: When using Ceph, use at least three monitors (MON) and three managers (MGR) to ensure high availability of the Ceph cluster.
Expert Tip: Before choosing a type of shared storage, evaluate the performance, reliability, and scalability requirements of your cluster. Test different options to choose the most suitable solution.
| Storage Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| NFS | Easy to configure | Low performance | For small clusters with low requirements |
| iSCSI | Higher performance than NFS | More complex configuration than NFS | For medium-sized clusters |
| Ceph | High performance, reliability and scalability | Complex configuration | For large clusters with high requirements |
Failover Configuration for Virtual Machines
After configuring shared storage, you need to configure Failover for virtual machines. Proxmox VE provides convenient tools for managing HA resources. In this section, we will look at how to enable and configure HA for virtual machines.
Enabling HA for a Virtual Machine
1. Select the virtual machine for which you want to enable HA in the Proxmox VE web interface.
2. Go to the «HA» tab.
3. Click the «Enable HA» button.
4. Configure HA parameters:
- Priority: The priority of the virtual machine during Failover. Virtual machines with higher priority will be restarted first.
- Group: Virtual machine group. Virtual machines in the same group will be restarted together.
- Max Relocate: The maximum number of attempts to restart the virtual machine on another node.
- Max Restart: The maximum number of restarts of the virtual machine on the same node.
5. Save your changes.
Managing HA Resources Using the Command Line
Proxmox VE also provides command-line tools for managing HA resources. This can be useful for automating HA configuration or troubleshooting.
1. Adding an HA resource:
ha-manager add vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager add vm:1002. Removing an HA resource:
ha-manager remove vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager remove vm:1003. Changing HA resource parameters:
ha-manager set vm:<VMID> --priority <priority> --group <group>For example:
ha-manager set vm:100 --priority 2 --group mygroup4. Viewing the HA cluster status:
ha-manager statusRecommendations for Configuring HA
1. Assign priorities to virtual machines depending on their importance. Critical virtual machines should have a higher priority.
2. Use groups to combine virtual machines that should be restarted together. For example, if a web application consists of multiple virtual machines (web server, database), combine them into one group.
3. Configure the Max Relocate and Max Restart parameters according to the requirements of your applications. Too many restart attempts can lead to cluster instability.
4. Monitor the HA cluster status using the web interface or command line. Make sure that all virtual machines are in the «started» state and that Failover is working correctly.
Example 1: If you have a virtual machine with a database that is critical for the operation of the website, assign it a high priority (for example, 50).
Example 2: If you have two virtual machines that work together (for example, a web server and an application server), combine them into one group (for example, webapp).
Example 3: If a virtual machine often fails, increase the Max Restart value so that Proxmox VE tries to restart it several times before giving up.
Expert Tip: Carefully plan your Failover strategy. Determine which virtual machines are the most critical and configure HA according to their requirements. Regularly test Failover to ensure that it is working.
Testing and Maintaining a High Availability Cluster
After setting up an HA cluster, you need to regularly test its performance and perform maintenance. This will ensure that Failover works correctly and that the cluster is ready for real failures. In this section, we will look at testing methods and recommendations for maintaining an HA cluster.
Failover Testing Methods
- Simulating a server failure: The easiest way to test Failover is to simulate a server failure. To do this, you can turn off one of the cluster nodes or cause a critical error that will cause it to reboot.
- Virtual machine migration: Check how quickly and smoothly the migration of a virtual machine from one node to another occurs.
- Checking the availability of services: Make sure that after Failover, all services running on the virtual machine remain available to users.
- Log analysis: Analyze the logs of Proxmox VE and other cluster components to make sure that Failover has passed without errors.
Example 1: To simulate a server failure, you can use the command shutdown -h now on one of the cluster nodes.
shutdown -h nowExample 2: To migrate a virtual machine, you can use the Proxmox VE web interface. Select a virtual machine and click the «Migrate» button.
Example 3: After Failover, check that the website running on the virtual machine is still available at its IP address or domain name.
Recommendations for Maintaining an HA Cluster
- Regularly update the software: Install the latest updates for Proxmox VE, operating systems on virtual machines, and other cluster components.
- Monitor the cluster status: Use monitoring tools such as Zabbix or Prometheus to track the status of cluster nodes, resource usage, and other important parameters.
- Perform backups: Regularly back up virtual machines and cluster configuration files.
- Check the performance of shared storage: Make sure that shared storage is accessible to all cluster nodes and that there is enough free space on it.
- Document all changes: Keep documentation of all changes made to the cluster configuration. This will help in troubleshooting and maintaining the cluster.
Example 1: Configure automatic backup of virtual machines using the built-in Proxmox VE tools or other backup solutions.
Example 2: Use Zabbix to monitor CPU load, memory usage, and disk space on all cluster nodes.
Example 3: Regularly check the Proxmox VE logs for errors or warnings. The logs are located in the /var/log/ directory.
tail -f /var/log/syslogExpert Tip: Create a Disaster Recovery Plan for your HA cluster. This plan should describe all the steps that need to be taken in the event of a serious failure that leads to data loss or cluster unavailability.
High availability is not just a technology, it is a process. Regular testing and maintenance are key factors for ensuring reliable operation of an HA cluster.
Author: John Doe, Senior Systems Administrator
4. Discover the iSCSI Target using the iscsiadm command.
5. Connect the LUN to each Proxmox VE node.
6. Add an iSCSI storage in Proxmox VE. In the Proxmox VE web interface, select «Datacenter» -> «Storage» -> «Add» -> «iSCSI». Specify the Target, LUN, and other required parameters.
Configuring Ceph
Ceph is the most complex, but also the most productive and reliable solution for shared storage. Configuring Ceph is beyond the scope of this article and requires a separate guide. Proxmox VE has built-in integration with Ceph, which simplifies the setup process.
Example 1: When using NFS, make sure that the latest version is installed on the NFS server. Older versions of NFS may have performance and security issues.
Example 2: When using iSCSI, use CHAP (Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol) to authenticate between the iSCSI Initiator and Target. This will increase storage security.
Example 3: When using Ceph, use at least three monitors (MON) and three managers (MGR) to ensure high availability of the Ceph cluster.
Expert Tip: Before choosing a type of shared storage, evaluate the performance, reliability, and scalability requirements of your cluster. Test different options to choose the most suitable solution.
| Storage Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| NFS | Easy to configure | Low performance | For small clusters with low requirements |
| iSCSI | Higher performance than NFS | More complex configuration than NFS | For medium-sized clusters |
| Ceph | High performance, reliability and scalability | Complex configuration | For large clusters with high requirements |
Failover Configuration for Virtual Machines
After configuring shared storage, you need to configure Failover for virtual machines. Proxmox VE provides convenient tools for managing HA resources. In this section, we will look at how to enable and configure HA for virtual machines.
Enabling HA for a Virtual Machine
1. Select the virtual machine for which you want to enable HA in the Proxmox VE web interface.
2. Go to the «HA» tab.
3. Click the «Enable HA» button.
4. Configure HA parameters:
- Priority: The priority of the virtual machine during Failover. Virtual machines with higher priority will be restarted first.
- Group: Virtual machine group. Virtual machines in the same group will be restarted together.
- Max Relocate: The maximum number of attempts to restart the virtual machine on another node.
- Max Restart: The maximum number of restarts of the virtual machine on the same node.
5. Save your changes.
Managing HA Resources Using the Command Line
Proxmox VE also provides command-line tools for managing HA resources. This can be useful for automating HA configuration or troubleshooting.
1. Adding an HA resource:
ha-manager add vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager add vm:1002. Removing an HA resource:
ha-manager remove vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager remove vm:1003. Changing HA resource parameters:
ha-manager set vm:<VMID> --priority <priority> --group <group>For example:
ha-manager set vm:100 --priority 2 --group mygroup4. Viewing the HA cluster status:
ha-manager statusRecommendations for Configuring HA
1. Assign priorities to virtual machines depending on their importance. Critical virtual machines should have a higher priority.
2. Use groups to combine virtual machines that should be restarted together. For example, if a web application consists of multiple virtual machines (web server, database), combine them into one group.
3. Configure the Max Relocate and Max Restart parameters according to the requirements of your applications. Too many restart attempts can lead to cluster instability.
4. Monitor the HA cluster status using the web interface or command line. Make sure that all virtual machines are in the «started» state and that Failover is working correctly.
Example 1: If you have a virtual machine with a database that is critical for the operation of the website, assign it a high priority (for example, 50).
Example 2: If you have two virtual machines that work together (for example, a web server and an application server), combine them into one group (for example, webapp).
Example 3: If a virtual machine often fails, increase the Max Restart value so that Proxmox VE tries to restart it several times before giving up.
Expert Tip: Carefully plan your Failover strategy. Determine which virtual machines are the most critical and configure HA according to their requirements. Regularly test Failover to ensure that it is working.
Testing and Maintaining a High Availability Cluster
After setting up an HA cluster, you need to regularly test its performance and perform maintenance. This will ensure that Failover works correctly and that the cluster is ready for real failures. In this section, we will look at testing methods and recommendations for maintaining an HA cluster.
Failover Testing Methods
- Simulating a server failure: The easiest way to test Failover is to simulate a server failure. To do this, you can turn off one of the cluster nodes or cause a critical error that will cause it to reboot.
- Virtual machine migration: Check how quickly and smoothly the migration of a virtual machine from one node to another occurs.
- Checking the availability of services: Make sure that after Failover, all services running on the virtual machine remain available to users.
- Log analysis: Analyze the logs of Proxmox VE and other cluster components to make sure that Failover has passed without errors.
Example 1: To simulate a server failure, you can use the command shutdown -h now on one of the cluster nodes.
shutdown -h nowExample 2: To migrate a virtual machine, you can use the Proxmox VE web interface. Select a virtual machine and click the «Migrate» button.
Example 3: After Failover, check that the website running on the virtual machine is still available at its IP address or domain name.
Recommendations for Maintaining an HA Cluster
- Regularly update the software: Install the latest updates for Proxmox VE, operating systems on virtual machines, and other cluster components.
- Monitor the cluster status: Use monitoring tools such as Zabbix or Prometheus to track the status of cluster nodes, resource usage, and other important parameters.
- Perform backups: Regularly back up virtual machines and cluster configuration files.
- Check the performance of shared storage: Make sure that shared storage is accessible to all cluster nodes and that there is enough free space on it.
- Document all changes: Keep documentation of all changes made to the cluster configuration. This will help in troubleshooting and maintaining the cluster.
Example 1: Configure automatic backup of virtual machines using the built-in Proxmox VE tools or other backup solutions.
Example 2: Use Zabbix to monitor CPU load, memory usage, and disk space on all cluster nodes.
Example 3: Regularly check the Proxmox VE logs for errors or warnings. The logs are located in the /var/log/ directory.
tail -f /var/log/syslogExpert Tip: Create a Disaster Recovery Plan for your HA cluster. This plan should describe all the steps that need to be taken in the event of a serious failure that leads to data loss or cluster unavailability.
High availability is not just a technology, it is a process. Regular testing and maintenance are key factors for ensuring reliable operation of an HA cluster.
Author: John Doe, Senior Systems Administrator
4. Discover the iSCSI Target using the iscsiadm command.
5. Connect the LUN to each Proxmox VE node.
6. Add an iSCSI storage in Proxmox VE. In the Proxmox VE web interface, select «Datacenter» -> «Storage» -> «Add» -> «iSCSI». Specify the Target, LUN, and other required parameters.
Configuring Ceph
Ceph is the most complex, but also the most productive and reliable solution for shared storage. Configuring Ceph is beyond the scope of this article and requires a separate guide. Proxmox VE has built-in integration with Ceph, which simplifies the setup process.
Example 1: When using NFS, make sure that the latest version is installed on the NFS server. Older versions of NFS may have performance and security issues.
Example 2: When using iSCSI, use CHAP (Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol) to authenticate between the iSCSI Initiator and Target. This will increase storage security.
Example 3: When using Ceph, use at least three monitors (MON) and three managers (MGR) to ensure high availability of the Ceph cluster.
Expert Tip: Before choosing a type of shared storage, evaluate the performance, reliability, and scalability requirements of your cluster. Test different options to choose the most suitable solution.
| Storage Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| NFS | Easy to configure | Low performance | For small clusters with low requirements |
| iSCSI | Higher performance than NFS | More complex configuration than NFS | For medium-sized clusters |
| Ceph | High performance, reliability and scalability | Complex configuration | For large clusters with high requirements |
Failover Configuration for Virtual Machines
After configuring shared storage, you need to configure Failover for virtual machines. Proxmox VE provides convenient tools for managing HA resources. In this section, we will look at how to enable and configure HA for virtual machines.
Enabling HA for a Virtual Machine
1. Select the virtual machine for which you want to enable HA in the Proxmox VE web interface.
2. Go to the «HA» tab.
3. Click the «Enable HA» button.
4. Configure HA parameters:
- Priority: The priority of the virtual machine during Failover. Virtual machines with higher priority will be restarted first.
- Group: Virtual machine group. Virtual machines in the same group will be restarted together.
- Max Relocate: The maximum number of attempts to restart the virtual machine on another node.
- Max Restart: The maximum number of restarts of the virtual machine on the same node.
5. Save your changes.
Managing HA Resources Using the Command Line
Proxmox VE also provides command-line tools for managing HA resources. This can be useful for automating HA configuration or troubleshooting.
1. Adding an HA resource:
ha-manager add vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager add vm:1002. Removing an HA resource:
ha-manager remove vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager remove vm:1003. Changing HA resource parameters:
ha-manager set vm:<VMID> --priority <priority> --group <group>For example:
ha-manager set vm:100 --priority 2 --group mygroup4. Viewing the HA cluster status:
ha-manager statusRecommendations for Configuring HA
1. Assign priorities to virtual machines depending on their importance. Critical virtual machines should have a higher priority.
2. Use groups to combine virtual machines that should be restarted together. For example, if a web application consists of multiple virtual machines (web server, database), combine them into one group.
3. Configure the Max Relocate and Max Restart parameters according to the requirements of your applications. Too many restart attempts can lead to cluster instability.
4. Monitor the HA cluster status using the web interface or command line. Make sure that all virtual machines are in the «started» state and that Failover is working correctly.
Example 1: If you have a virtual machine with a database that is critical for the operation of the website, assign it a high priority (for example, 50).
Example 2: If you have two virtual machines that work together (for example, a web server and an application server), combine them into one group (for example, webapp).
Example 3: If a virtual machine often fails, increase the Max Restart value so that Proxmox VE tries to restart it several times before giving up.
Expert Tip: Carefully plan your Failover strategy. Determine which virtual machines are the most critical and configure HA according to their requirements. Regularly test Failover to ensure that it is working.
Testing and Maintaining a High Availability Cluster
After setting up an HA cluster, you need to regularly test its performance and perform maintenance. This will ensure that Failover works correctly and that the cluster is ready for real failures. In this section, we will look at testing methods and recommendations for maintaining an HA cluster.
Failover Testing Methods
- Simulating a server failure: The easiest way to test Failover is to simulate a server failure. To do this, you can turn off one of the cluster nodes or cause a critical error that will cause it to reboot.
- Virtual machine migration: Check how quickly and smoothly the migration of a virtual machine from one node to another occurs.
- Checking the availability of services: Make sure that after Failover, all services running on the virtual machine remain available to users.
- Log analysis: Analyze the logs of Proxmox VE and other cluster components to make sure that Failover has passed without errors.
Example 1: To simulate a server failure, you can use the command shutdown -h now on one of the cluster nodes.
shutdown -h nowExample 2: To migrate a virtual machine, you can use the Proxmox VE web interface. Select a virtual machine and click the «Migrate» button.
Example 3: After Failover, check that the website running on the virtual machine is still available at its IP address or domain name.
Recommendations for Maintaining an HA Cluster
- Regularly update the software: Install the latest updates for Proxmox VE, operating systems on virtual machines, and other cluster components.
- Monitor the cluster status: Use monitoring tools such as Zabbix or Prometheus to track the status of cluster nodes, resource usage, and other important parameters.
- Perform backups: Regularly back up virtual machines and cluster configuration files.
- Check the performance of shared storage: Make sure that shared storage is accessible to all cluster nodes and that there is enough free space on it.
- Document all changes: Keep documentation of all changes made to the cluster configuration. This will help in troubleshooting and maintaining the cluster.
Example 1: Configure automatic backup of virtual machines using the built-in Proxmox VE tools or other backup solutions.
Example 2: Use Zabbix to monitor CPU load, memory usage, and disk space on all cluster nodes.
Example 3: Regularly check the Proxmox VE logs for errors or warnings. The logs are located in the /var/log/ directory.
tail -f /var/log/syslogExpert Tip: Create a Disaster Recovery Plan for your HA cluster. This plan should describe all the steps that need to be taken in the event of a serious failure that leads to data loss or cluster unavailability.
High availability is not just a technology, it is a process. Regular testing and maintenance are key factors for ensuring reliable operation of an HA cluster.
Author: John Doe, Senior Systems Administrator
2. Create a LUN (Logical Unit Number) on the storage server.
3. Configure the iSCSI Initiator on each Proxmox VE node. For example, on Debian/Ubuntu:
apt update
apt install open-iscsi4. Discover the iSCSI Target using the iscsiadm command.
5. Connect the LUN to each Proxmox VE node.
6. Add an iSCSI storage in Proxmox VE. In the Proxmox VE web interface, select «Datacenter» -> «Storage» -> «Add» -> «iSCSI». Specify the Target, LUN, and other required parameters.
Configuring Ceph
Ceph is the most complex, but also the most productive and reliable solution for shared storage. Configuring Ceph is beyond the scope of this article and requires a separate guide. Proxmox VE has built-in integration with Ceph, which simplifies the setup process.
Example 1: When using NFS, make sure that the latest version is installed on the NFS server. Older versions of NFS may have performance and security issues.
Example 2: When using iSCSI, use CHAP (Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol) to authenticate between the iSCSI Initiator and Target. This will increase storage security.
Example 3: When using Ceph, use at least three monitors (MON) and three managers (MGR) to ensure high availability of the Ceph cluster.
Expert Tip: Before choosing a type of shared storage, evaluate the performance, reliability, and scalability requirements of your cluster. Test different options to choose the most suitable solution.
| Storage Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| NFS | Easy to configure | Low performance | For small clusters with low requirements |
| iSCSI | Higher performance than NFS | More complex configuration than NFS | For medium-sized clusters |
| Ceph | High performance, reliability and scalability | Complex configuration | For large clusters with high requirements |
Failover Configuration for Virtual Machines
After configuring shared storage, you need to configure Failover for virtual machines. Proxmox VE provides convenient tools for managing HA resources. In this section, we will look at how to enable and configure HA for virtual machines.
Enabling HA for a Virtual Machine
1. Select the virtual machine for which you want to enable HA in the Proxmox VE web interface.
2. Go to the «HA» tab.
3. Click the «Enable HA» button.
4. Configure HA parameters:
- Priority: The priority of the virtual machine during Failover. Virtual machines with higher priority will be restarted first.
- Group: Virtual machine group. Virtual machines in the same group will be restarted together.
- Max Relocate: The maximum number of attempts to restart the virtual machine on another node.
- Max Restart: The maximum number of restarts of the virtual machine on the same node.
5. Save your changes.
Managing HA Resources Using the Command Line
Proxmox VE also provides command-line tools for managing HA resources. This can be useful for automating HA configuration or troubleshooting.
1. Adding an HA resource:
ha-manager add vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager add vm:1002. Removing an HA resource:
ha-manager remove vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager remove vm:1003. Changing HA resource parameters:
ha-manager set vm:<VMID> --priority <priority> --group <group>For example:
ha-manager set vm:100 --priority 2 --group mygroup4. Viewing the HA cluster status:
ha-manager statusRecommendations for Configuring HA
1. Assign priorities to virtual machines depending on their importance. Critical virtual machines should have a higher priority.
2. Use groups to combine virtual machines that should be restarted together. For example, if a web application consists of multiple virtual machines (web server, database), combine them into one group.
3. Configure the Max Relocate and Max Restart parameters according to the requirements of your applications. Too many restart attempts can lead to cluster instability.
4. Monitor the HA cluster status using the web interface or command line. Make sure that all virtual machines are in the «started» state and that Failover is working correctly.
Example 1: If you have a virtual machine with a database that is critical for the operation of the website, assign it a high priority (for example, 50).
Example 2: If you have two virtual machines that work together (for example, a web server and an application server), combine them into one group (for example, webapp).
Example 3: If a virtual machine often fails, increase the Max Restart value so that Proxmox VE tries to restart it several times before giving up.
Expert Tip: Carefully plan your Failover strategy. Determine which virtual machines are the most critical and configure HA according to their requirements. Regularly test Failover to ensure that it is working.
Testing and Maintaining a High Availability Cluster
After setting up an HA cluster, you need to regularly test its performance and perform maintenance. This will ensure that Failover works correctly and that the cluster is ready for real failures. In this section, we will look at testing methods and recommendations for maintaining an HA cluster.
Failover Testing Methods
- Simulating a server failure: The easiest way to test Failover is to simulate a server failure. To do this, you can turn off one of the cluster nodes or cause a critical error that will cause it to reboot.
- Virtual machine migration: Check how quickly and smoothly the migration of a virtual machine from one node to another occurs.
- Checking the availability of services: Make sure that after Failover, all services running on the virtual machine remain available to users.
- Log analysis: Analyze the logs of Proxmox VE and other cluster components to make sure that Failover has passed without errors.
Example 1: To simulate a server failure, you can use the command shutdown -h now on one of the cluster nodes.
shutdown -h nowExample 2: To migrate a virtual machine, you can use the Proxmox VE web interface. Select a virtual machine and click the «Migrate» button.
Example 3: After Failover, check that the website running on the virtual machine is still available at its IP address or domain name.
Recommendations for Maintaining an HA Cluster
- Regularly update the software: Install the latest updates for Proxmox VE, operating systems on virtual machines, and other cluster components.
- Monitor the cluster status: Use monitoring tools such as Zabbix or Prometheus to track the status of cluster nodes, resource usage, and other important parameters.
- Perform backups: Regularly back up virtual machines and cluster configuration files.
- Check the performance of shared storage: Make sure that shared storage is accessible to all cluster nodes and that there is enough free space on it.
- Document all changes: Keep documentation of all changes made to the cluster configuration. This will help in troubleshooting and maintaining the cluster.
Example 1: Configure automatic backup of virtual machines using the built-in Proxmox VE tools or other backup solutions.
Example 2: Use Zabbix to monitor CPU load, memory usage, and disk space on all cluster nodes.
Example 3: Regularly check the Proxmox VE logs for errors or warnings. The logs are located in the /var/log/ directory.
tail -f /var/log/syslogExpert Tip: Create a Disaster Recovery Plan for your HA cluster. This plan should describe all the steps that need to be taken in the event of a serious failure that leads to data loss or cluster unavailability.
High availability is not just a technology, it is a process. Regular testing and maintenance are key factors for ensuring reliable operation of an HA cluster.
Author: John Doe, Senior Systems Administrator
2. Create a LUN (Logical Unit Number) on the storage server.
3. Configure the iSCSI Initiator on each Proxmox VE node. For example, on Debian/Ubuntu:
apt update
apt install open-iscsi4. Discover the iSCSI Target using the iscsiadm command.
5. Connect the LUN to each Proxmox VE node.
6. Add an iSCSI storage in Proxmox VE. In the Proxmox VE web interface, select «Datacenter» -> «Storage» -> «Add» -> «iSCSI». Specify the Target, LUN, and other required parameters.
Configuring Ceph
Ceph is the most complex, but also the most productive and reliable solution for shared storage. Configuring Ceph is beyond the scope of this article and requires a separate guide. Proxmox VE has built-in integration with Ceph, which simplifies the setup process.
Example 1: When using NFS, make sure that the latest version is installed on the NFS server. Older versions of NFS may have performance and security issues.
Example 2: When using iSCSI, use CHAP (Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol) to authenticate between the iSCSI Initiator and Target. This will increase storage security.
Example 3: When using Ceph, use at least three monitors (MON) and three managers (MGR) to ensure high availability of the Ceph cluster.
Expert Tip: Before choosing a type of shared storage, evaluate the performance, reliability, and scalability requirements of your cluster. Test different options to choose the most suitable solution.
| Storage Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| NFS | Easy to configure | Low performance | For small clusters with low requirements |
| iSCSI | Higher performance than NFS | More complex configuration than NFS | For medium-sized clusters |
| Ceph | High performance, reliability and scalability | Complex configuration | For large clusters with high requirements |
Failover Configuration for Virtual Machines
After configuring shared storage, you need to configure Failover for virtual machines. Proxmox VE provides convenient tools for managing HA resources. In this section, we will look at how to enable and configure HA for virtual machines.
Enabling HA for a Virtual Machine
1. Select the virtual machine for which you want to enable HA in the Proxmox VE web interface.
2. Go to the «HA» tab.
3. Click the «Enable HA» button.
4. Configure HA parameters:
- Priority: The priority of the virtual machine during Failover. Virtual machines with higher priority will be restarted first.
- Group: Virtual machine group. Virtual machines in the same group will be restarted together.
- Max Relocate: The maximum number of attempts to restart the virtual machine on another node.
- Max Restart: The maximum number of restarts of the virtual machine on the same node.
5. Save your changes.
Managing HA Resources Using the Command Line
Proxmox VE also provides command-line tools for managing HA resources. This can be useful for automating HA configuration or troubleshooting.
1. Adding an HA resource:
ha-manager add vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager add vm:1002. Removing an HA resource:
ha-manager remove vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager remove vm:1003. Changing HA resource parameters:
ha-manager set vm:<VMID> --priority <priority> --group <group>For example:
ha-manager set vm:100 --priority 2 --group mygroup4. Viewing the HA cluster status:
ha-manager statusRecommendations for Configuring HA
1. Assign priorities to virtual machines depending on their importance. Critical virtual machines should have a higher priority.
2. Use groups to combine virtual machines that should be restarted together. For example, if a web application consists of multiple virtual machines (web server, database), combine them into one group.
3. Configure the Max Relocate and Max Restart parameters according to the requirements of your applications. Too many restart attempts can lead to cluster instability.
4. Monitor the HA cluster status using the web interface or command line. Make sure that all virtual machines are in the «started» state and that Failover is working correctly.
Example 1: If you have a virtual machine with a database that is critical for the operation of the website, assign it a high priority (for example, 50).
Example 2: If you have two virtual machines that work together (for example, a web server and an application server), combine them into one group (for example, webapp).
Example 3: If a virtual machine often fails, increase the Max Restart value so that Proxmox VE tries to restart it several times before giving up.
Expert Tip: Carefully plan your Failover strategy. Determine which virtual machines are the most critical and configure HA according to their requirements. Regularly test Failover to ensure that it is working.
Testing and Maintaining a High Availability Cluster
After setting up an HA cluster, you need to regularly test its performance and perform maintenance. This will ensure that Failover works correctly and that the cluster is ready for real failures. In this section, we will look at testing methods and recommendations for maintaining an HA cluster.
Failover Testing Methods
- Simulating a server failure: The easiest way to test Failover is to simulate a server failure. To do this, you can turn off one of the cluster nodes or cause a critical error that will cause it to reboot.
- Virtual machine migration: Check how quickly and smoothly the migration of a virtual machine from one node to another occurs.
- Checking the availability of services: Make sure that after Failover, all services running on the virtual machine remain available to users.
- Log analysis: Analyze the logs of Proxmox VE and other cluster components to make sure that Failover has passed without errors.
Example 1: To simulate a server failure, you can use the command shutdown -h now on one of the cluster nodes.
shutdown -h nowExample 2: To migrate a virtual machine, you can use the Proxmox VE web interface. Select a virtual machine and click the «Migrate» button.
Example 3: After Failover, check that the website running on the virtual machine is still available at its IP address or domain name.
Recommendations for Maintaining an HA Cluster
- Regularly update the software: Install the latest updates for Proxmox VE, operating systems on virtual machines, and other cluster components.
- Monitor the cluster status: Use monitoring tools such as Zabbix or Prometheus to track the status of cluster nodes, resource usage, and other important parameters.
- Perform backups: Regularly back up virtual machines and cluster configuration files.
- Check the performance of shared storage: Make sure that shared storage is accessible to all cluster nodes and that there is enough free space on it.
- Document all changes: Keep documentation of all changes made to the cluster configuration. This will help in troubleshooting and maintaining the cluster.
Example 1: Configure automatic backup of virtual machines using the built-in Proxmox VE tools or other backup solutions.
Example 2: Use Zabbix to monitor CPU load, memory usage, and disk space on all cluster nodes.
Example 3: Regularly check the Proxmox VE logs for errors or warnings. The logs are located in the /var/log/ directory.
tail -f /var/log/syslogExpert Tip: Create a Disaster Recovery Plan for your HA cluster. This plan should describe all the steps that need to be taken in the event of a serious failure that leads to data loss or cluster unavailability.
High availability is not just a technology, it is a process. Regular testing and maintenance are key factors for ensuring reliable operation of an HA cluster.
Author: John Doe, Senior Systems Administrator
Configuring iSCSI is much more complex than NFS and requires a separate detailed instruction.
1. Install iSCSI Target on the storage server. For example, on Debian/Ubuntu, you can use tgt.
apt update
apt install tgt2. Create a LUN (Logical Unit Number) on the storage server.
3. Configure the iSCSI Initiator on each Proxmox VE node. For example, on Debian/Ubuntu:
apt update
apt install open-iscsi4. Discover the iSCSI Target using the iscsiadm command.
5. Connect the LUN to each Proxmox VE node.
6. Add an iSCSI storage in Proxmox VE. In the Proxmox VE web interface, select «Datacenter» -> «Storage» -> «Add» -> «iSCSI». Specify the Target, LUN, and other required parameters.
Configuring Ceph
Ceph is the most complex, but also the most productive and reliable solution for shared storage. Configuring Ceph is beyond the scope of this article and requires a separate guide. Proxmox VE has built-in integration with Ceph, which simplifies the setup process.
Example 1: When using NFS, make sure that the latest version is installed on the NFS server. Older versions of NFS may have performance and security issues.
Example 2: When using iSCSI, use CHAP (Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol) to authenticate between the iSCSI Initiator and Target. This will increase storage security.
Example 3: When using Ceph, use at least three monitors (MON) and three managers (MGR) to ensure high availability of the Ceph cluster.
Expert Tip: Before choosing a type of shared storage, evaluate the performance, reliability, and scalability requirements of your cluster. Test different options to choose the most suitable solution.
| Storage Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| NFS | Easy to configure | Low performance | For small clusters with low requirements |
| iSCSI | Higher performance than NFS | More complex configuration than NFS | For medium-sized clusters |
| Ceph | High performance, reliability and scalability | Complex configuration | For large clusters with high requirements |
Failover Configuration for Virtual Machines
After configuring shared storage, you need to configure Failover for virtual machines. Proxmox VE provides convenient tools for managing HA resources. In this section, we will look at how to enable and configure HA for virtual machines.
Enabling HA for a Virtual Machine
1. Select the virtual machine for which you want to enable HA in the Proxmox VE web interface.
2. Go to the «HA» tab.
3. Click the «Enable HA» button.
4. Configure HA parameters:
- Priority: The priority of the virtual machine during Failover. Virtual machines with higher priority will be restarted first.
- Group: Virtual machine group. Virtual machines in the same group will be restarted together.
- Max Relocate: The maximum number of attempts to restart the virtual machine on another node.
- Max Restart: The maximum number of restarts of the virtual machine on the same node.
5. Save your changes.
Managing HA Resources Using the Command Line
Proxmox VE also provides command-line tools for managing HA resources. This can be useful for automating HA configuration or troubleshooting.
1. Adding an HA resource:
ha-manager add vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager add vm:1002. Removing an HA resource:
ha-manager remove vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager remove vm:1003. Changing HA resource parameters:
ha-manager set vm:<VMID> --priority <priority> --group <group>For example:
ha-manager set vm:100 --priority 2 --group mygroup4. Viewing the HA cluster status:
ha-manager statusRecommendations for Configuring HA
1. Assign priorities to virtual machines depending on their importance. Critical virtual machines should have a higher priority.
2. Use groups to combine virtual machines that should be restarted together. For example, if a web application consists of multiple virtual machines (web server, database), combine them into one group.
3. Configure the Max Relocate and Max Restart parameters according to the requirements of your applications. Too many restart attempts can lead to cluster instability.
4. Monitor the HA cluster status using the web interface or command line. Make sure that all virtual machines are in the «started» state and that Failover is working correctly.
Example 1: If you have a virtual machine with a database that is critical for the operation of the website, assign it a high priority (for example, 50).
Example 2: If you have two virtual machines that work together (for example, a web server and an application server), combine them into one group (for example, webapp).
Example 3: If a virtual machine often fails, increase the Max Restart value so that Proxmox VE tries to restart it several times before giving up.
Expert Tip: Carefully plan your Failover strategy. Determine which virtual machines are the most critical and configure HA according to their requirements. Regularly test Failover to ensure that it is working.
Testing and Maintaining a High Availability Cluster
After setting up an HA cluster, you need to regularly test its performance and perform maintenance. This will ensure that Failover works correctly and that the cluster is ready for real failures. In this section, we will look at testing methods and recommendations for maintaining an HA cluster.
Failover Testing Methods
- Simulating a server failure: The easiest way to test Failover is to simulate a server failure. To do this, you can turn off one of the cluster nodes or cause a critical error that will cause it to reboot.
- Virtual machine migration: Check how quickly and smoothly the migration of a virtual machine from one node to another occurs.
- Checking the availability of services: Make sure that after Failover, all services running on the virtual machine remain available to users.
- Log analysis: Analyze the logs of Proxmox VE and other cluster components to make sure that Failover has passed without errors.
Example 1: To simulate a server failure, you can use the command shutdown -h now on one of the cluster nodes.
shutdown -h nowExample 2: To migrate a virtual machine, you can use the Proxmox VE web interface. Select a virtual machine and click the «Migrate» button.
Example 3: After Failover, check that the website running on the virtual machine is still available at its IP address or domain name.
Recommendations for Maintaining an HA Cluster
- Regularly update the software: Install the latest updates for Proxmox VE, operating systems on virtual machines, and other cluster components.
- Monitor the cluster status: Use monitoring tools such as Zabbix or Prometheus to track the status of cluster nodes, resource usage, and other important parameters.
- Perform backups: Regularly back up virtual machines and cluster configuration files.
- Check the performance of shared storage: Make sure that shared storage is accessible to all cluster nodes and that there is enough free space on it.
- Document all changes: Keep documentation of all changes made to the cluster configuration. This will help in troubleshooting and maintaining the cluster.
Example 1: Configure automatic backup of virtual machines using the built-in Proxmox VE tools or other backup solutions.
Example 2: Use Zabbix to monitor CPU load, memory usage, and disk space on all cluster nodes.
Example 3: Regularly check the Proxmox VE logs for errors or warnings. The logs are located in the /var/log/ directory.
tail -f /var/log/syslogExpert Tip: Create a Disaster Recovery Plan for your HA cluster. This plan should describe all the steps that need to be taken in the event of a serious failure that leads to data loss or cluster unavailability.
High availability is not just a technology, it is a process. Regular testing and maintenance are key factors for ensuring reliable operation of an HA cluster.
Author: John Doe, Senior Systems Administrator
Configuring iSCSI is much more complex than NFS and requires a separate detailed instruction.
1. Install iSCSI Target on the storage server. For example, on Debian/Ubuntu, you can use tgt.
apt update
apt install tgt2. Create a LUN (Logical Unit Number) on the storage server.
3. Configure the iSCSI Initiator on each Proxmox VE node. For example, on Debian/Ubuntu:
apt update
apt install open-iscsi4. Discover the iSCSI Target using the iscsiadm command.
5. Connect the LUN to each Proxmox VE node.
6. Add an iSCSI storage in Proxmox VE. In the Proxmox VE web interface, select «Datacenter» -> «Storage» -> «Add» -> «iSCSI». Specify the Target, LUN, and other required parameters.
Configuring Ceph
Ceph is the most complex, but also the most productive and reliable solution for shared storage. Configuring Ceph is beyond the scope of this article and requires a separate guide. Proxmox VE has built-in integration with Ceph, which simplifies the setup process.
Example 1: When using NFS, make sure that the latest version is installed on the NFS server. Older versions of NFS may have performance and security issues.
Example 2: When using iSCSI, use CHAP (Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol) to authenticate between the iSCSI Initiator and Target. This will increase storage security.
Example 3: When using Ceph, use at least three monitors (MON) and three managers (MGR) to ensure high availability of the Ceph cluster.
Expert Tip: Before choosing a type of shared storage, evaluate the performance, reliability, and scalability requirements of your cluster. Test different options to choose the most suitable solution.
| Storage Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| NFS | Easy to configure | Low performance | For small clusters with low requirements |
| iSCSI | Higher performance than NFS | More complex configuration than NFS | For medium-sized clusters |
| Ceph | High performance, reliability and scalability | Complex configuration | For large clusters with high requirements |
Failover Configuration for Virtual Machines
After configuring shared storage, you need to configure Failover for virtual machines. Proxmox VE provides convenient tools for managing HA resources. In this section, we will look at how to enable and configure HA for virtual machines.
Enabling HA for a Virtual Machine
1. Select the virtual machine for which you want to enable HA in the Proxmox VE web interface.
2. Go to the «HA» tab.
3. Click the «Enable HA» button.
4. Configure HA parameters:
- Priority: The priority of the virtual machine during Failover. Virtual machines with higher priority will be restarted first.
- Group: Virtual machine group. Virtual machines in the same group will be restarted together.
- Max Relocate: The maximum number of attempts to restart the virtual machine on another node.
- Max Restart: The maximum number of restarts of the virtual machine on the same node.
5. Save your changes.
Managing HA Resources Using the Command Line
Proxmox VE also provides command-line tools for managing HA resources. This can be useful for automating HA configuration or troubleshooting.
1. Adding an HA resource:
ha-manager add vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager add vm:1002. Removing an HA resource:
ha-manager remove vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager remove vm:1003. Changing HA resource parameters:
ha-manager set vm:<VMID> --priority <priority> --group <group>For example:
ha-manager set vm:100 --priority 2 --group mygroup4. Viewing the HA cluster status:
ha-manager statusRecommendations for Configuring HA
1. Assign priorities to virtual machines depending on their importance. Critical virtual machines should have a higher priority.
2. Use groups to combine virtual machines that should be restarted together. For example, if a web application consists of multiple virtual machines (web server, database), combine them into one group.
3. Configure the Max Relocate and Max Restart parameters according to the requirements of your applications. Too many restart attempts can lead to cluster instability.
4. Monitor the HA cluster status using the web interface or command line. Make sure that all virtual machines are in the «started» state and that Failover is working correctly.
Example 1: If you have a virtual machine with a database that is critical for the operation of the website, assign it a high priority (for example, 50).
Example 2: If you have two virtual machines that work together (for example, a web server and an application server), combine them into one group (for example, webapp).
Example 3: If a virtual machine often fails, increase the Max Restart value so that Proxmox VE tries to restart it several times before giving up.
Expert Tip: Carefully plan your Failover strategy. Determine which virtual machines are the most critical and configure HA according to their requirements. Regularly test Failover to ensure that it is working.
Testing and Maintaining a High Availability Cluster
After setting up an HA cluster, you need to regularly test its performance and perform maintenance. This will ensure that Failover works correctly and that the cluster is ready for real failures. In this section, we will look at testing methods and recommendations for maintaining an HA cluster.
Failover Testing Methods
- Simulating a server failure: The easiest way to test Failover is to simulate a server failure. To do this, you can turn off one of the cluster nodes or cause a critical error that will cause it to reboot.
- Virtual machine migration: Check how quickly and smoothly the migration of a virtual machine from one node to another occurs.
- Checking the availability of services: Make sure that after Failover, all services running on the virtual machine remain available to users.
- Log analysis: Analyze the logs of Proxmox VE and other cluster components to make sure that Failover has passed without errors.
Example 1: To simulate a server failure, you can use the command shutdown -h now on one of the cluster nodes.
shutdown -h nowExample 2: To migrate a virtual machine, you can use the Proxmox VE web interface. Select a virtual machine and click the «Migrate» button.
Example 3: After Failover, check that the website running on the virtual machine is still available at its IP address or domain name.
Recommendations for Maintaining an HA Cluster
- Regularly update the software: Install the latest updates for Proxmox VE, operating systems on virtual machines, and other cluster components.
- Monitor the cluster status: Use monitoring tools such as Zabbix or Prometheus to track the status of cluster nodes, resource usage, and other important parameters.
- Perform backups: Regularly back up virtual machines and cluster configuration files.
- Check the performance of shared storage: Make sure that shared storage is accessible to all cluster nodes and that there is enough free space on it.
- Document all changes: Keep documentation of all changes made to the cluster configuration. This will help in troubleshooting and maintaining the cluster.
Example 1: Configure automatic backup of virtual machines using the built-in Proxmox VE tools or other backup solutions.
Example 2: Use Zabbix to monitor CPU load, memory usage, and disk space on all cluster nodes.
Example 3: Regularly check the Proxmox VE logs for errors or warnings. The logs are located in the /var/log/ directory.
tail -f /var/log/syslogExpert Tip: Create a Disaster Recovery Plan for your HA cluster. This plan should describe all the steps that need to be taken in the event of a serious failure that leads to data loss or cluster unavailability.
High availability is not just a technology, it is a process. Regular testing and maintenance are key factors for ensuring reliable operation of an HA cluster.
Author: John Doe, Senior Systems Administrator
How to Set Up High Availability for Virtual Machines: Failover Cluster Using Proxmox VE as an Example
Ensuring the continuous operation of critical services is a priority for any business. High Availability (HA) of virtual machines allows you to minimize downtime and guarantee the stable operation of applications. In this article, we will take a detailed look at how to configure a high availability cluster for virtual machines using Proxmox VE as an example, focusing on the Failover mechanism.
We will examine the necessary components, setup steps, and testing methods so that you can create a fault-tolerant virtualization infrastructure on your own.
- Introduction to High Availability and Failover
- Installation and Basic Configuration of Proxmox VE for HA
- Configuring Shared Storage for an HA Cluster
- Failover Configuration for Virtual Machines
- Testing and Maintaining a High Availability Cluster
Introduction to High Availability and Failover
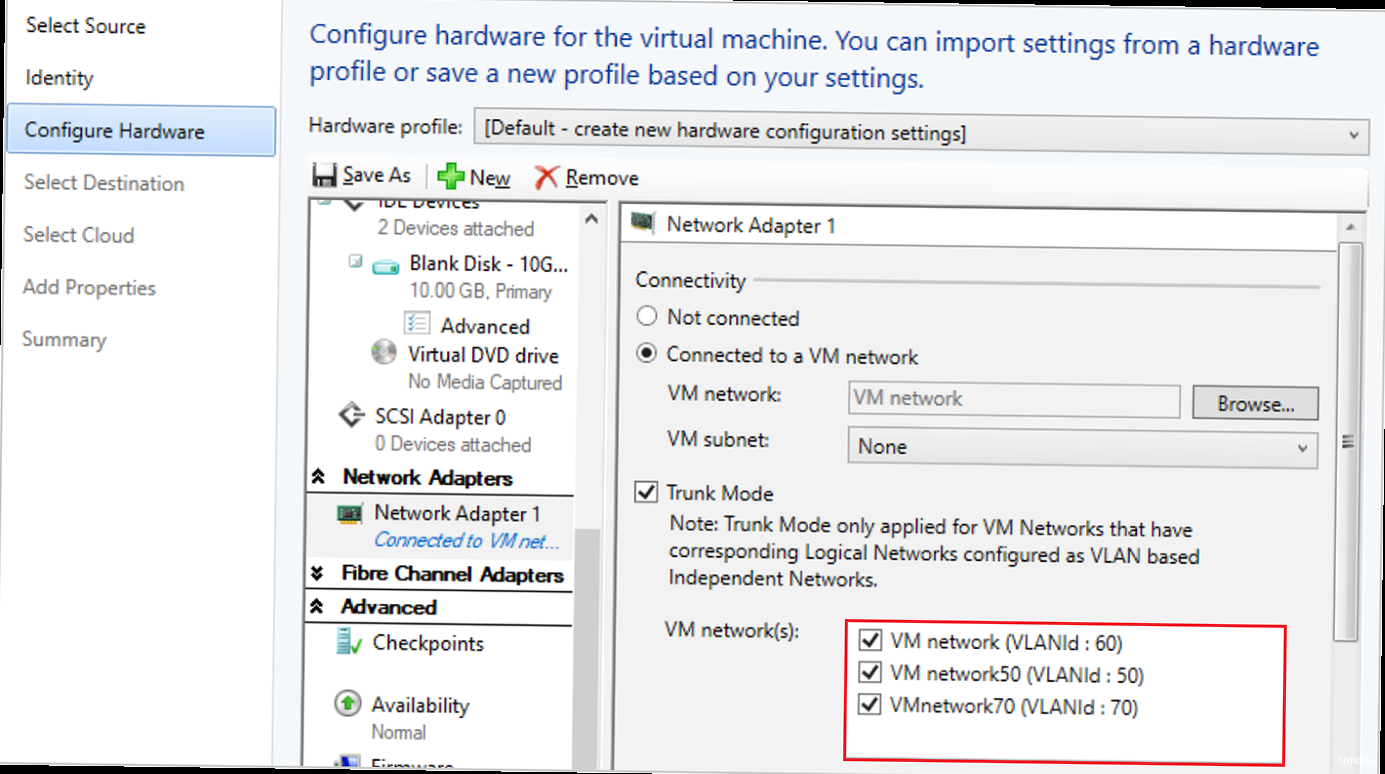
High Availability (HA) is the ability of a system to continue functioning even if one or more components fail. This is achieved by reserving resources and automatically switching to backup components in the event of a failure. The main goal of HA is to minimize downtime and ensure the continuous operation of critical services.
Failover is a mechanism for automatically switching to a backup system or component in the event of a primary failure. In the context of virtualization, Failover means automatically restarting a virtual machine on another physical server (node) of the cluster if the original server fails. This process should be as fast and transparent as possible for users.
Using HA clusters provides many advantages:
- Minimizing downtime: Automatic Failover ensures rapid restoration of virtual machine performance.
- Increased reliability: Resource redundancy eliminates a single point of failure.
- Improved maintenance: Ability to perform planned work (e.g., server updates) without interrupting services.
- Protection against hardware failures: Automatic switching to backup servers in the event of hardware failure.
Key Components of an HA Cluster
The following components are required to build an HA cluster:
- Multiple physical servers (nodes): To ensure resource redundancy.
- Shared storage: Must be accessible to all cluster nodes and contain virtual machine images.
- Clustering software: Provides cluster management, node status monitoring, and automatic Failover. (e.g., Proxmox VE)
- Network with high bandwidth and low latency: For data exchange between cluster nodes and access to shared storage.
Example 1: Imagine we have a virtual machine with an important web server. Without HA, if the server on which this VM is running fails, the website becomes unavailable until the server is restored. With HA, this VM will automatically restart on another server in the cluster, minimizing downtime.
Example 2: In Proxmox VE, the HA cluster is managed by built-in tools. The system automatically tracks the status of each VM and node. When a failure is detected, Proxmox VE initiates Failover, transferring the VM to a healthy node.
Example 3: You can use NFS, iSCSI, Ceph, or GlusterFS for shared storage. It is important that the storage is reliable and provides high performance so as not to create a bottleneck in the HA cluster.
Expert Tip: When planning an HA cluster, consider possible failure scenarios. Think about which VMs are the most critical and require maximum protection. It is also important to regularly test Failover to ensure that it is working.
Installation and Basic Configuration of Proxmox VE for HA
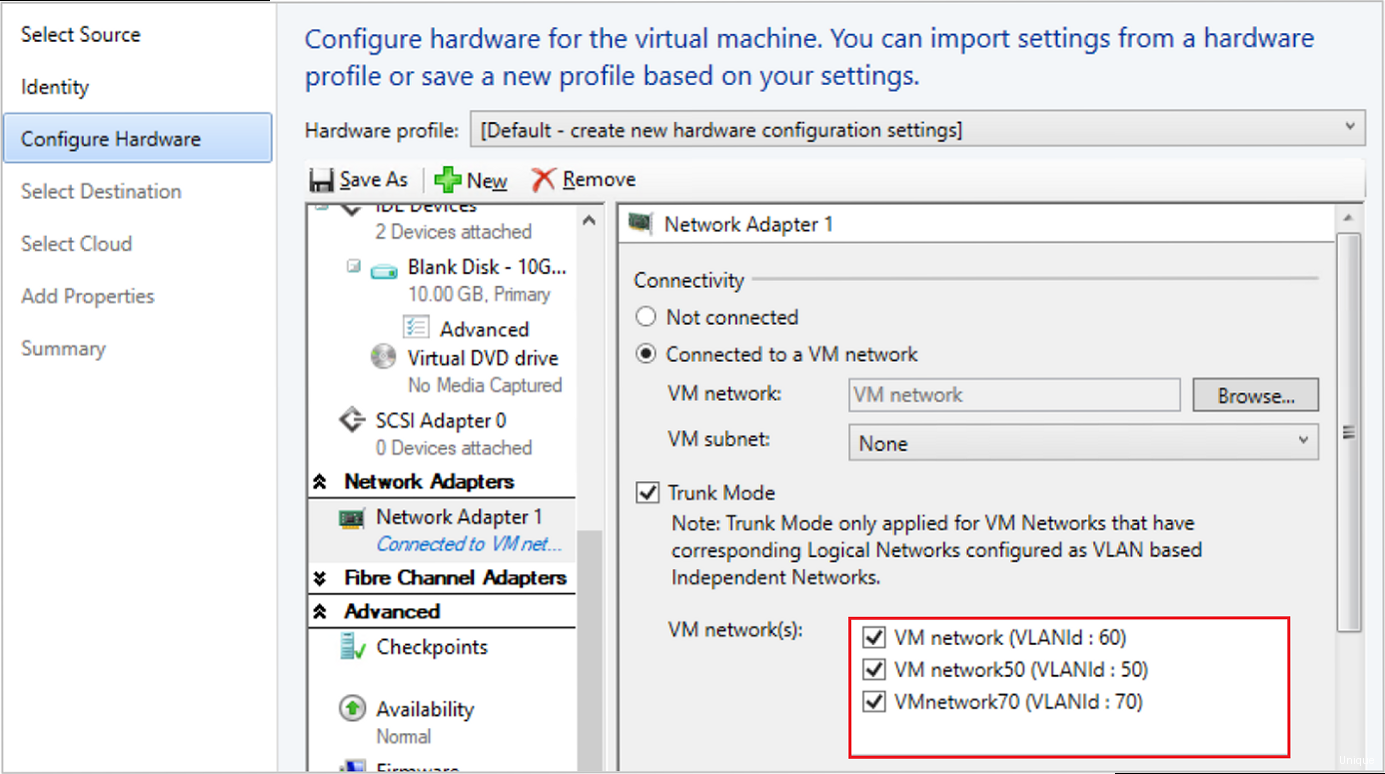
Before you begin setting up an HA cluster, you need to install and configure Proxmox VE on all the physical servers that will be part of the cluster. In this section, we will look at the main steps of installation and basic configuration.
Installing Proxmox VE
1. Download the Proxmox VE ISO image from the official website: https://www.proxmox.com/en/downloads.
2. Write the ISO image to a USB drive or DVD. You can use tools like Rufus or Etcher to write.
3. Boot from the USB drive or DVD on each server on which Proxmox VE will be installed.
4. Follow the installer instructions. During the installation process, you must specify the following parameters:
- Language and keyboard layout
- Time zone
- Administrator password (root) Network settings (servers with IP addresses, network mask, gateway, DNS servers)
- Hard disk partition to install Proxmox VE
5. After the installation is complete, reboot the server.
Basic Configuration of Proxmox VE
After installation, you need to perform the basic configuration of Proxmox VE. Connect to the Proxmox VE web interface using the IP address specified during installation (for example, https://192.168.1.100:8006).
1. Update the system. Open the console (Shell) in the web interface and run the following commands:
apt update
apt upgrade2. Configure the host name. Make sure each server has a unique host name. Modify the /etc/hosts and /etc/hostname files if necessary. For example:
nano /etc/hosts
nano /etc/hostname3. Configure network interfaces. Make sure that all servers have access to the network and can communicate with each other. Configure the /etc/network/interfaces file if necessary. Example:
nano /etc/network/interfacesExample contents of the /etc/network/interfaces file:
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
iface enp3s0 inet manual
auto vmbr0
iface vmbr0 inet static
address 192.168.1.100
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.1.1
bridge-ports enp3s0
bridge-stp off
bridge-fd 04. Create a Proxmox VE cluster. Run the following command on one of the servers:
pvecm create <cluster_name>For example:
pvecm create mycluster5. Join the remaining servers to the cluster. Run the following command on each of the remaining servers:
pvecm add <IP_address_of_the_first_server>For example:
pvecm add 192.168.1.100You will need to enter the administrator (root) password of the first server during the addition process.
6. Check the cluster status. Run the command on any of the servers:
pvecm statusMake sure that all servers are displayed in the list and have the status «online».
Example 1: After installing Proxmox VE, it is important to update the system immediately. This will ensure the installation of the latest security patches and improvements.
Example 2: When creating a cluster, make sure that all servers have synchronized time. You can use NTP (Network Time Protocol) for this. Install and configure NTP on all servers.
Example 3: When adding servers to a cluster, make sure that a reliable network is used. It is recommended to use a dedicated network for data exchange between cluster nodes.
Expert Tip: Before creating a cluster, carefully plan your network configuration. Incorrect network settings can lead to problems with Failover and cluster stability.
Configuring Shared Storage for an HA Cluster
Shared storage is a critical component of an HA cluster. It must be accessible to all cluster nodes and contain virtual machine images, as well as their configuration files. In this section, we will look at various types of shared storage and methods for configuring them in Proxmox VE.
Types of Shared Storage
- NFS (Network File System): A simple and common solution. Suitable for small clusters with low performance requirements. iSCSI (Internet Small Computer System Interface): A more productive solution than NFS. Requires configuring an iSCSI Target on the storage servers and an iSCSI Initiator on each Proxmox VE node.
- Ceph: A distributed data storage system that provides high availability and scalability. Requires more complex configuration, but provides better performance and reliability.
- GlusterFS: Another distributed data storage system similar to Ceph.
Configuring NFS
1. Install the NFS server on the server that will provide shared storage. For example, on Debian/Ubuntu:
apt update
apt install nfs-kernel-server2. Create a directory to store virtual machine images:
mkdir /mnt/pve/shared3. Configure directory exporting. Edit the /etc/exports file:
nano /etc/exportsAdd the following line:
/mnt/pve/shared 192.168.1.0/24(rw,sync,no_subtree_check)Where 192.168.1.0/24 is your subnet.
4. Export changes:
exportfs -a5. Restart the NFS server:
systemctl restart nfs-kernel-server6. Add an NFS storage in Proxmox VE. In the Proxmox VE web interface, select «Datacenter» -> «Storage» -> «Add» -> «NFS». Specify the IP address of the NFS server, the path to the exported directory, and the storage ID.
Configuring iSCSI
Configuring iSCSI is much more complex than NFS and requires a separate detailed instruction.
1. Install iSCSI Target on the storage server. For example, on Debian/Ubuntu, you can use tgt.
apt update
apt install tgt2. Create a LUN (Logical Unit Number) on the storage server.
3. Configure the iSCSI Initiator on each Proxmox VE node. For example, on Debian/Ubuntu:
apt update
apt install open-iscsi4. Discover the iSCSI Target using the iscsiadm command.
5. Connect the LUN to each Proxmox VE node.
6. Add an iSCSI storage in Proxmox VE. In the Proxmox VE web interface, select «Datacenter» -> «Storage» -> «Add» -> «iSCSI». Specify the Target, LUN, and other required parameters.
Configuring Ceph
Ceph is the most complex, but also the most productive and reliable solution for shared storage. Configuring Ceph is beyond the scope of this article and requires a separate guide. Proxmox VE has built-in integration with Ceph, which simplifies the setup process.
Example 1: When using NFS, make sure that the latest version is installed on the NFS server. Older versions of NFS may have performance and security issues.
Example 2: When using iSCSI, use CHAP (Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol) to authenticate between the iSCSI Initiator and Target. This will increase storage security.
Example 3: When using Ceph, use at least three monitors (MON) and three managers (MGR) to ensure high availability of the Ceph cluster.
Expert Tip: Before choosing a type of shared storage, evaluate the performance, reliability, and scalability requirements of your cluster. Test different options to choose the most suitable solution.
| Storage Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| NFS | Easy to configure | Low performance | For small clusters with low requirements |
| iSCSI | Higher performance than NFS | More complex configuration than NFS | For medium-sized clusters |
| Ceph | High performance, reliability and scalability | Complex configuration | For large clusters with high requirements |
Failover Configuration for Virtual Machines
After configuring shared storage, you need to configure Failover for virtual machines. Proxmox VE provides convenient tools for managing HA resources. In this section, we will look at how to enable and configure HA for virtual machines.
Enabling HA for a Virtual Machine
1. Select the virtual machine for which you want to enable HA in the Proxmox VE web interface.
2. Go to the «HA» tab.
3. Click the «Enable HA» button.
4. Configure HA parameters:
- Priority: The priority of the virtual machine during Failover. Virtual machines with higher priority will be restarted first.
- Group: Virtual machine group. Virtual machines in the same group will be restarted together.
- Max Relocate: The maximum number of attempts to restart the virtual machine on another node.
- Max Restart: The maximum number of restarts of the virtual machine on the same node.
5. Save your changes.
Managing HA Resources Using the Command Line
Proxmox VE also provides command-line tools for managing HA resources. This can be useful for automating HA configuration or troubleshooting.
1. Adding an HA resource:
ha-manager add vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager add vm:1002. Removing an HA resource:
ha-manager remove vm:<VMID>For example:
ha-manager remove vm:1003. Changing HA resource parameters:
ha-manager set vm:<VMID> --priority <priority> --group <group>For example:
ha-manager set vm:100 --priority 2 --group mygroup4. Viewing the HA cluster status:
ha-manager statusRecommendations for Configuring HA
1. Assign priorities to virtual machines depending on their importance. Critical virtual machines should have a higher priority.
2. Use groups to combine virtual machines that should be restarted together. For example, if a web application consists of multiple virtual machines (web server, database), combine them into one group.
3. Configure the Max Relocate and Max Restart parameters according to the requirements of your applications. Too many restart attempts can lead to cluster instability.
4. Monitor the HA cluster status using the web interface or command line. Make sure that all virtual machines are in the «started» state and that Failover is working correctly.
Example 1: If you have a virtual machine with a database that is critical for the operation of the website, assign it a high priority (for example, 50).
Example 2: If you have two virtual machines that work together (for example, a web server and an application server), combine them into one group (for example, webapp).
Example 3: If a virtual machine often fails, increase the Max Restart value so that Proxmox VE tries to restart it several times before giving up.
Expert Tip: Carefully plan your Failover strategy. Determine which virtual machines are the most critical and configure HA according to their requirements. Regularly test Failover to ensure that it is working.
Testing and Maintaining a High Availability Cluster
After setting up an HA cluster, you need to regularly test its performance and perform maintenance. This will ensure that Failover works correctly and that the cluster is ready for real failures. In this section, we will look at testing methods and recommendations for maintaining an HA cluster.
Failover Testing Methods
- Simulating a server failure: The easiest way to test Failover is to simulate a server failure. To do this, you can turn off one of the cluster nodes or cause a critical error that will cause it to reboot.
- Virtual machine migration: Check how quickly and smoothly the migration of a virtual machine from one node to another occurs.
- Checking the availability of services: Make sure that after Failover, all services running on the virtual machine remain available to users.
- Log analysis: Analyze the logs of Proxmox VE and other cluster components to make sure that Failover has passed without errors.
Example 1: To simulate a server failure, you can use the command shutdown -h now on one of the cluster nodes.
shutdown -h nowExample 2: To migrate a virtual machine, you can use the Proxmox VE web interface. Select a virtual machine and click the «Migrate» button.
Example 3: After Failover, check that the website running on the virtual machine is still available at its IP address or domain name.
Recommendations for Maintaining an HA Cluster
- Regularly update the software: Install the latest updates for Proxmox VE, operating systems on virtual machines, and other cluster components.
- Monitor the cluster status: Use monitoring tools such as Zabbix or Prometheus to track the status of cluster nodes, resource usage, and other important parameters.
- Perform backups: Regularly back up virtual machines and cluster configuration files.
- Check the performance of shared storage: Make sure that shared storage is accessible to all cluster nodes and that there is enough free space on it.
- Document all changes: Keep documentation of all changes made to the cluster configuration. This will help in troubleshooting and maintaining the cluster.
Example 1: Configure automatic backup of virtual machines using the built-in Proxmox VE tools or other backup solutions.
Example 2: Use Zabbix to monitor CPU load, memory usage, and disk space on all cluster nodes.
Example 3: Regularly check the Proxmox VE logs for errors or warnings. The logs are located in the /var/log/ directory.
tail -f /var/log/syslogExpert Tip: Create a Disaster Recovery Plan for your HA cluster. This plan should describe all the steps that need to be taken in the event of a serious failure that leads to data loss or cluster unavailability.
High availability is not just a technology, it is a process. Regular testing and maintenance are key factors for ensuring reliable operation of an HA cluster.
Author: John Doe, Senior Systems Administrator