Configuring a RAID Array on a Dedicated HP ProLiant Server
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a technology that allows you to combine multiple hard drives into a single logical array to protect data and improve storage performance. This article will guide you through the process of setting up a RAID array on a dedicated HP ProLiant server.
Step 1: Connecting to the Server
First, you need to connect to your dedicated HP ProLiant server using remote access. You can use remote management tools like iLO (Integrated Lights-Out) or HP Integrated Remote Console (IRC).
After successfully connecting to the server, you need to enter the BIOS and configure the parameters for creating a RAID array.
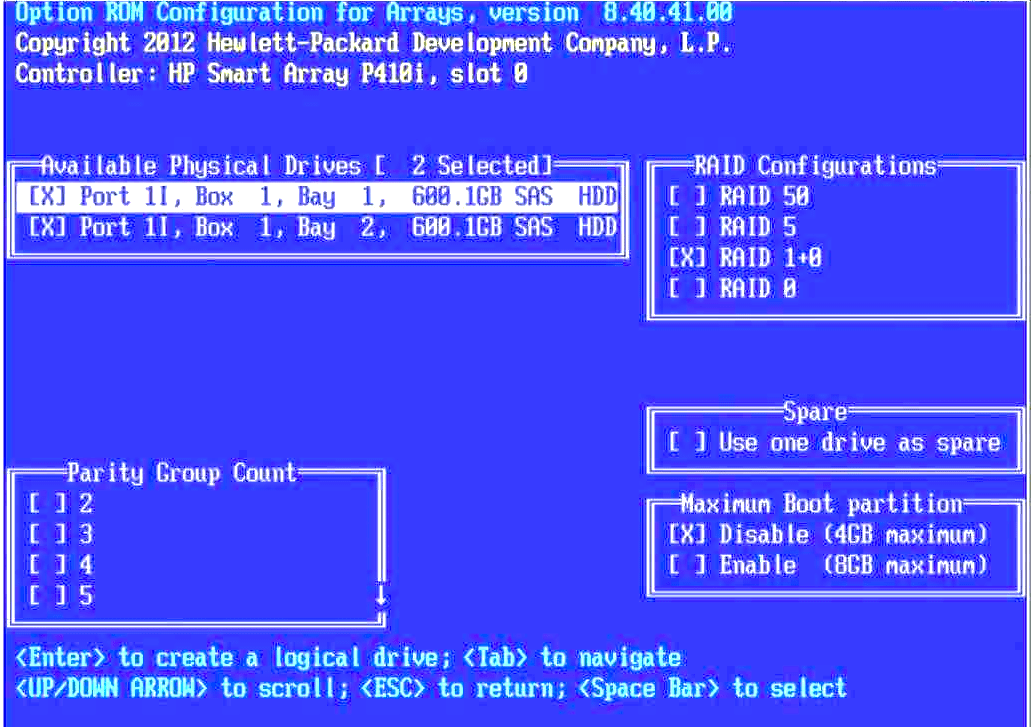
Step 2: Creating the RAID Array
To create a RAID array, follow these steps:
- Boot into the BIOS by pressing the appropriate key during server startup (usually F2, F8, or Delete).
- Find the section responsible for array creation and select the «Create RAID Array» option.
- Choose the RAID type (e.g., RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, etc.) and specify the disks to be included in the array.
- Save the changes and exit the BIOS.
- Reboot the server to complete the RAID array creation process.
Step 3: Installing the OS on the RAID Array
After creating the RAID array, you need to install the operating system (OS) on it. This requires a bootable OS media and the RAID controller drivers.
During OS installation, pay attention to the partition you choose for installation. It’s usually found under «Advanced Options» or «Advanced Installation Options».
After completing the operating system installation, you should verify the RAID array’s functionality and configure data backups to ensure data security.
Conclusion
Configuring a RAID array on a dedicated HP ProLiant server is a crucial process that ensures data safety and reliable storage. By following the steps above, you can create a RAID array and protect the information on your server.
Remember to regularly check the RAID array’s status and perform data backups to avoid data loss in case of hardware failure or human error.