What’s Better: OpenVZ or KVM?
When choosing virtualization for your server, the question arises: what’s better – OpenVZ or KVM? Both technologies have their advantages and disadvantages, and the right choice depends on your specific needs. Let’s figure out which system will suit you best.
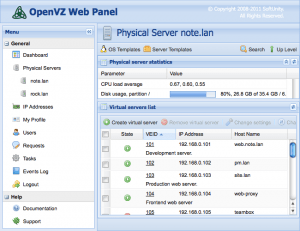
OpenVZ
OpenVZ is operating system-level containerization. It allows you to run multiple isolated containers on a single server with a shared kernel. The advantages of OpenVZ include high performance, low overhead, and ease of management. However, the disadvantage is the limitation in the choice of operating system – all containers must run on the same OS.
KVM
KVM is a hardware-assisted virtualization technology. It allows you to run virtual machines with separate kernels and resources. The advantages of KVM include the ability to run different operating systems on one server, complete isolation between virtual machines, and the ability to use specific kernels and kernel modules. However, the disadvantage is a higher load on the server and higher resource costs.
What to Choose?
When choosing between OpenVZ and KVM, you need to consider your needs and goals. If performance and ease of management are important to you, then OpenVZ may be the best option. If you value flexibility, the ability to run different operating systems, and complete isolation between virtual machines, then you should pay attention to KVM.
In the end, the choice between OpenVZ and KVM depends on your specific needs. Both technologies have their advantages and disadvantages, and it is important to carefully analyze your requirements before making a decision.
We hope this overview helps you make the right choice when choosing virtualization for your server.