How to Use LVM Snapshots for Backups?
When backing up data, it’s important to have a reliable and convenient tool that allows you to restore information in case of accidental deletion or corruption. One such tool is LVM snapshots.
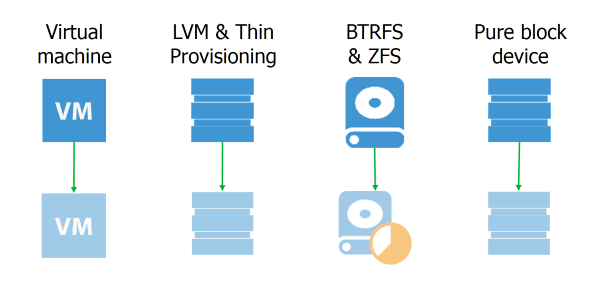
LVM (Logical Volume Manager) is a mechanism in Linux operating systems that allows you to manage data storage with more flexible capabilities than standard file systems.
LVM snapshots allow you to create exact copies of data volumes at a specific point in time. This is useful for backups because they capture the state of the data at a specific moment, without affecting the original data.
Let’s look at how to use LVM snapshots to create a data backup.
Step 1: Creating an LVM Snapshot
To create an LVM snapshot, you need to execute the following commands:
lvcreate --snapshot --name snapshot_name --size size_of_snapshot original_volume
Where:
- snapshot_name: the name of the snapshot you choose.
- size_of_snapshot: the size of the snapshot.
- original_volume: the original volume you are creating the snapshot for.
For example, to create a snapshot named my_snapshot with a size of 1GB for the volume /dev/my_volume, execute the following command:
lvcreate --snapshot --name my_snapshot --size 1G /dev/my_volume
Step 2: Working with the LVM Snapshot
After creating the LVM snapshot, you can perform operations on the data, knowing that the original data remains intact. For example, you can back up the snapshot to a remote server or to the cloud.
Step 3: Deleting an LVM Snapshot
Once you have finished working with the snapshot and no longer need it, you can safely delete it, freeing up disk space:
lvremove /dev/my_volume/my_snapshot
Thus, using LVM snapshots for data backup provides a convenient and reliable way to protect information. Remember to create snapshots regularly and store them in a safe place for emergencies.