How to Configure logrotate for Security?
Logs are an essential tool for tracking activity on your system. However, if you need to store a large amount of logs, this can lead to disk space exhaustion and increase security risks.
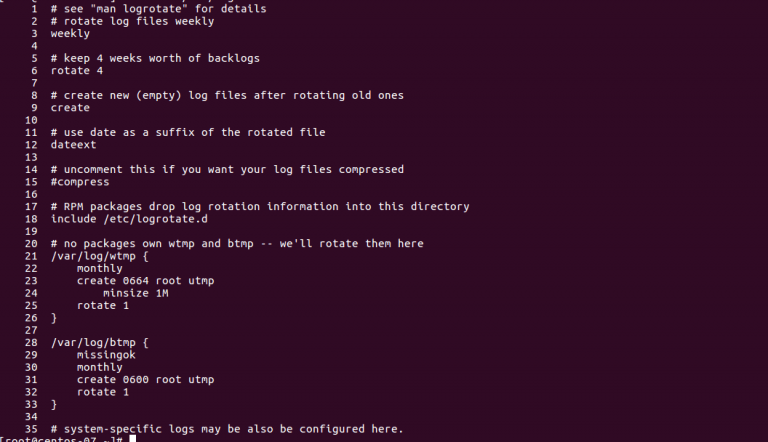
One way to solve this problem is to properly configure the logrotate utility. Logrotate is designed to automatically back up and archive log files, as well as rotate (clean up) them to optimize disk space usage.
Let’s look at how to configure logrotate to ensure the security of your system.
Step 1: Installing logrotate
The first step is to install the logrotate utility if it is not already installed. To do this, run the command:
sudo apt-get install logrotate
After successful installation, you can proceed to configure logrotate.
Step 2: Creating a Configuration File
Create a new configuration file for logrotate in the /etc/logrotate.d/ directory. For example, you can create an nginx file to rotate the logs of the Nginx web server:
sudo nano /etc/logrotate.d/nginx
Add the necessary settings for rotating Nginx logs to the created file.
Step 3: Configuring Rotation Parameters
Define the log rotation parameters in the created configuration file. Some of the main parameters include:
- daily — daily rotation
- rotate 7 — store the last 7 copies of logs
- compress — compress rotated logs
Configure the rotation parameters according to your needs.
Step 4: Testing the Configuration
Before running logrotate, it is recommended to test your configuration using the command:
sudo logrotate -d /etc/logrotate.d/nginx
This will allow you to check if there are any errors when rotating logs.
Step 5: Creating a cron Job
To automatically rotate logs according to your configuration, add a cron job. To do this, run the command:
sudo crontab -e
Add the following line to the cron file:
0 0 * * * /usr/sbin/logrotate /etc/logrotate.d/nginx
This will allow the log rotation to run daily at midnight.
Step 6: Automatic Cleanup of Old Logs
To prevent the accumulation of a large number of logs on the disk, configure parameters for automatically deleting old archives. For example, you can add the maxage 30 option to delete files older than 30 days:
/var/log/nginx/*.log {
daily
rotate 7
compress
maxage 30
}
Conclusion
Configuring logrotate is an important step to ensure security and optimize disk space usage in your system. By following the steps above, you can configure logrotate on your server and effectively manage log files.