How Does LXC Containerization Work?
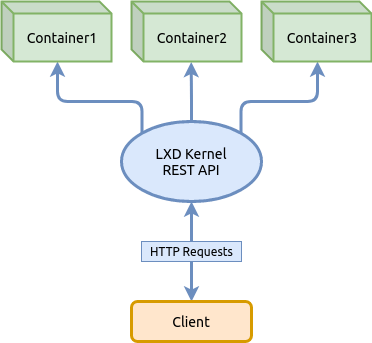
Containerization is a technology that allows you to package applications and all their dependencies into isolated containers. One of the popular tools for containerization in Linux is LXC (Linux Containers).
LXC provides the means to create and manage containers at the operating system level. Each container uses its own file system and is isolated from other containers and the main system.
So, how does LXC containerization work?
When you create a new container using LXC, it creates a new instance of the operating system kernel and an isolated environment for running applications. The container receives its own unique name and identifier, which is used to manage it.
The container uses namespaces technology to isolate various aspects of the operating system, such as the network, file system, and processes. This allows containers to operate as separate systems without affecting the main system.
In addition, LXC allows the use of cgroups to manage container resources, such as CPU, memory, and disk. This allows you to control and limit access to resources, which ensures stable and predictable operation of containers.
In conclusion, LXC containerization provides an efficient way to package and run applications in an isolated environment. It improves the security, scalability, and manageability of applications, making it a popular choice for Linux developers and administrators.